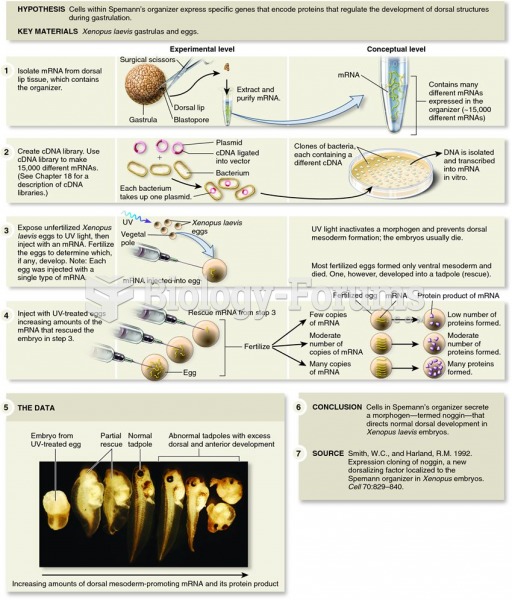
|
|
|
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
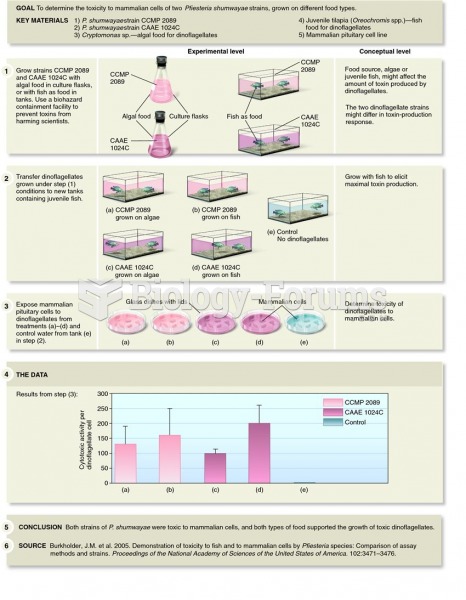 Burkholder and colleagues demonstrated that some strains of Pfiesteria shumwayae are toxic to fish a
Burkholder and colleagues demonstrated that some strains of Pfiesteria shumwayae are toxic to fish a
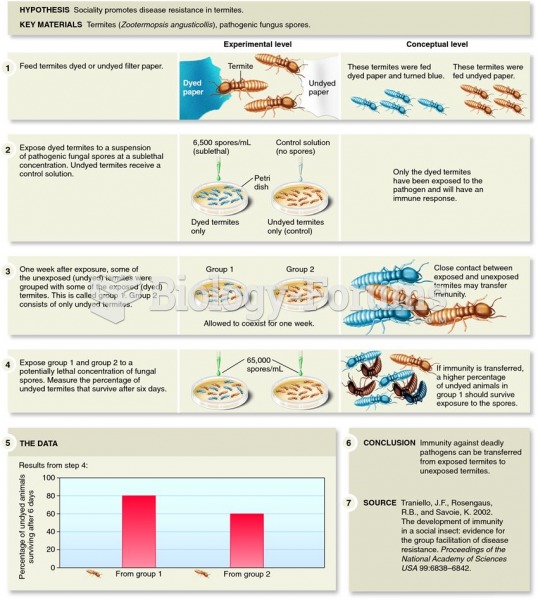 Traniello and his colleagues demonstrated that social insects may develop “social imm
Traniello and his colleagues demonstrated that social insects may develop “social imm
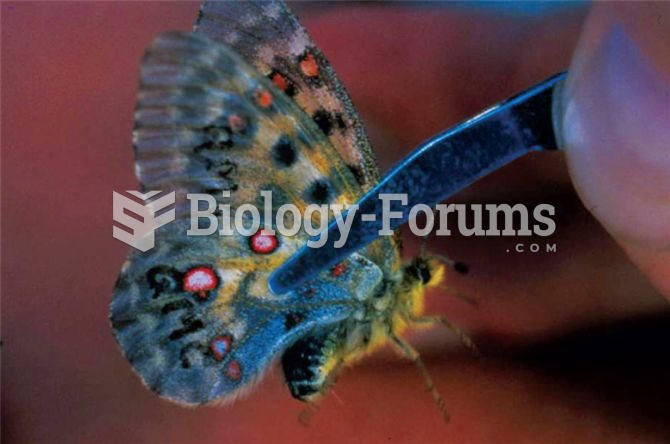 Jens Roland and colleagues marked (notice the QME on the wing) and recaptured many Rocky Mountain Pa
Jens Roland and colleagues marked (notice the QME on the wing) and recaptured many Rocky Mountain Pa