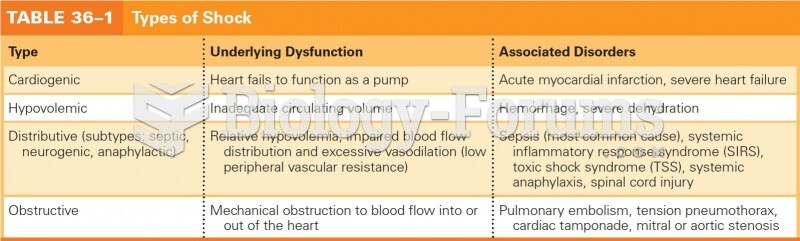
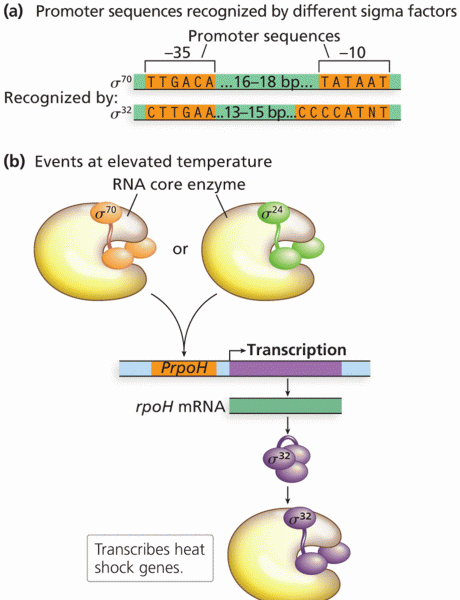
|
|
|
During the twentieth century, a variant of the metric system was used in Russia and France in which the base unit of mass was the tonne. Instead of kilograms, this system used millitonnes (mt).
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.