Answer to Question 1
A citator is a book or online service that provides the history and interpretation of a statute, regulation, or court decision and a list of the cases, statutes, and regulations that have interpreted, applied, or modified a statute or regulation. Citators are important to determine whether a case is still good law or whether it may be bad lawthat is, whether it has been reversed or modified on appeal.
Both Westlaw and Lexis provide online citators. In Lexis, the primary citator is Shepard's. Westlaw provides a similar service, called KeyCite.
Shepard's Citations has developed the most comprehensive system of case citators
in the United States. Shepard's lists every case published in an official or unofficial reporter by its citation. Every region of the National Reporter System, and more, is covered. Shepard's has been so widely used in the legal profession that the term Shepardizing means checking what has happened to a case over time. One of the most valuable functions of Shepard's is that it provides a means to verify the history
of a case. For example, if a paralegal wants to know whether a certain court decision has been reversed by a higher court, Shepard's provides that information. Shepard's is available in both printed and online (through Lexis) versions. It takes some time before the printed versions of Shepard's citators are updated, so a paralegal is most likely to use the online version to make sure his research is up to date.
Answer to Question 2
Both Westlaw and Lexis allow subscribers to locate documents using various search and browse methods. If you have the citation for a document, such as a court case or statute, you can enter the number and quickly call up the document. If you do not know the citation number, you can search according to legal topic, by case or party name, or by publication. If you do not know the best search terms to use for a particular search, both services will suggest terms to use. In both, you can search multiple sources simultaneously, and you can sort results by source type (cases, statutes and regulations, and law reviews and journals). In addition to using the search methods just described, you can locate documents with Westlaw using two different browsing methods. Westlaw's Table of Contents organizes the federal, state, and municipal laws of several countries into submenus, including both primary and secondary sources of law. Westlaw also allows you to browse a directory of laws, practice areas, periodicals, public records, news, and many other topics and subtopics arranged hierarchically into menus.
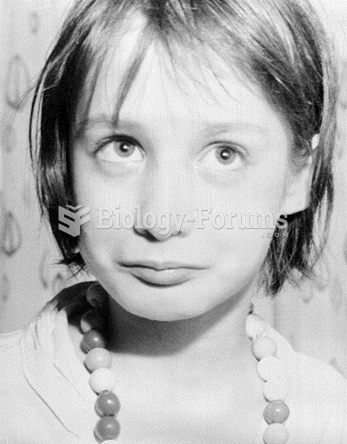 Some clues about the importance of language experience come from the tragic case of Genie, a girl ...
Some clues about the importance of language experience come from the tragic case of Genie, a girl ...
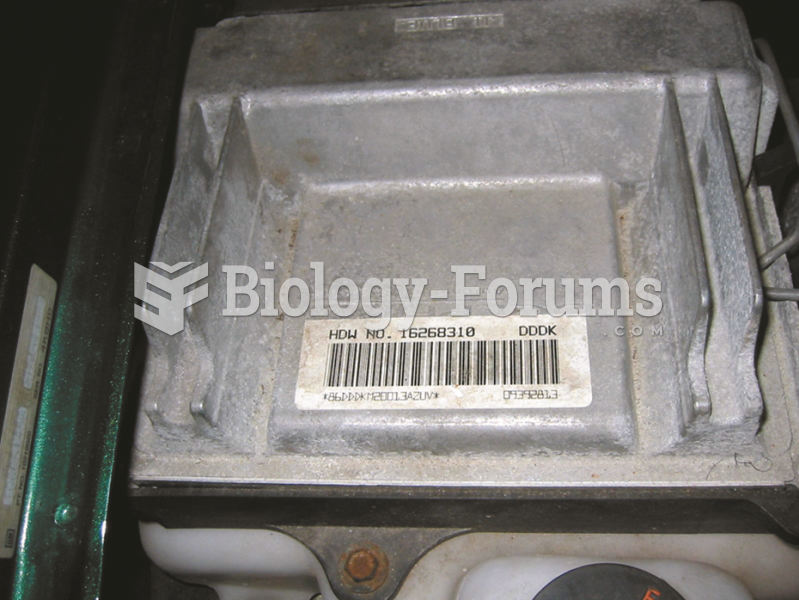 A typical calibration code sticker on the case of a controller. The information on the sticker is ...
A typical calibration code sticker on the case of a controller. The information on the sticker is ...