|
|
|
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
In the ancient and medieval periods, dysentery killed about ? of all babies before they reach 12 months of age. The disease was transferred through contaminated drinking water, because there was no way to adequately dispose of sewage, which contaminated the water.
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
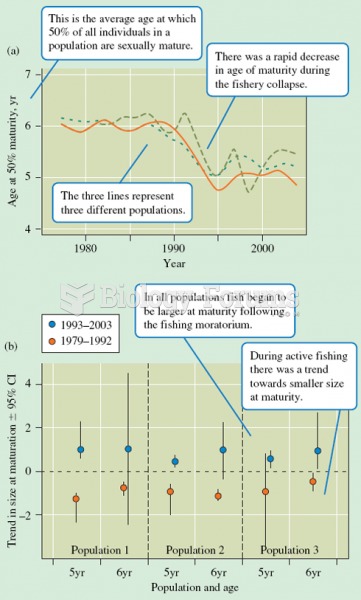 (a) Age of maturity of Atlantic cod decreased during the fishery collapse. (b) Evidence of maturatio
(a) Age of maturity of Atlantic cod decreased during the fishery collapse. (b) Evidence of maturatio
 As a result of sharing its environment with humans, this macaque had the opportunity to steal an ast
As a result of sharing its environment with humans, this macaque had the opportunity to steal an ast