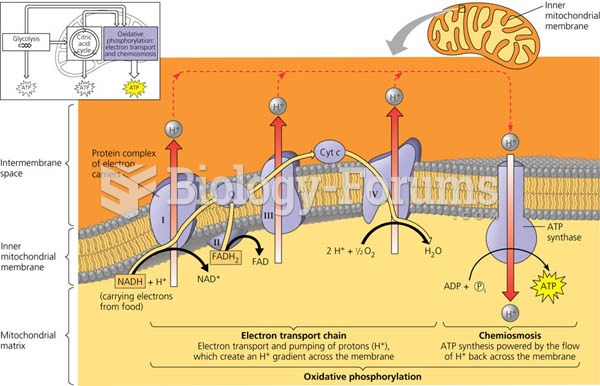
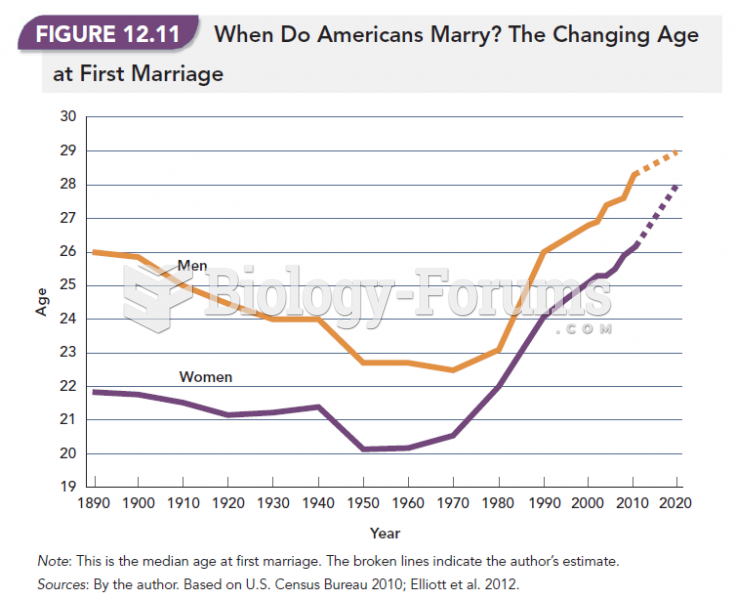
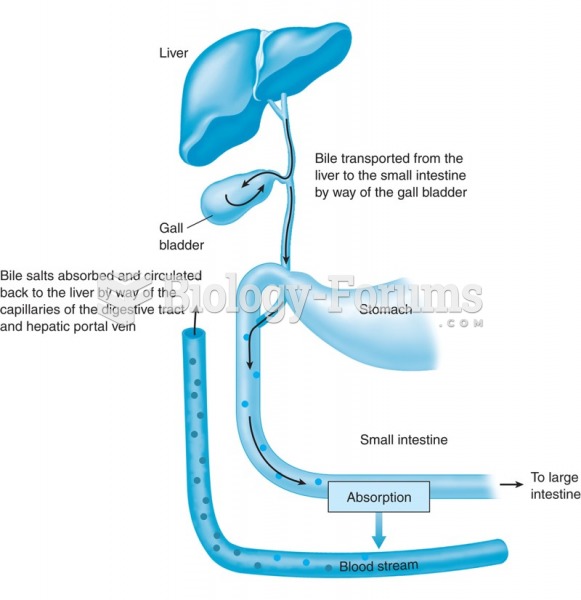
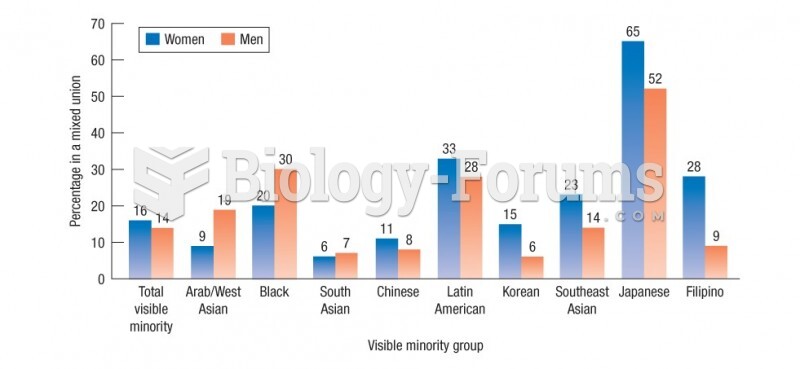
|
|
|
Parkinson's disease is both chronic and progressive. This means that it persists over a long period of time and that its symptoms grow worse over time.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
Recent studies have shown that the number of medication errors increases in relation to the number of orders that are verified per pharmacist, per work shift.
A strange skin disease referred to as Morgellons has occurred in the southern United States and in California. Symptoms include slowly healing sores, joint pain, persistent fatigue, and a sensation of things crawling through the skin. Another symptom is strange-looking, threadlike extrusions coming out of the skin.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Risperdal, an adult antipsychotic drug, for the symptomatic treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism. The approval is the first for the use of a drug to treat behaviors associated with autism in children. These behaviors are included under the general heading of irritability and include aggression, deliberate self-injury, and temper tantrums.