|
|
|
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
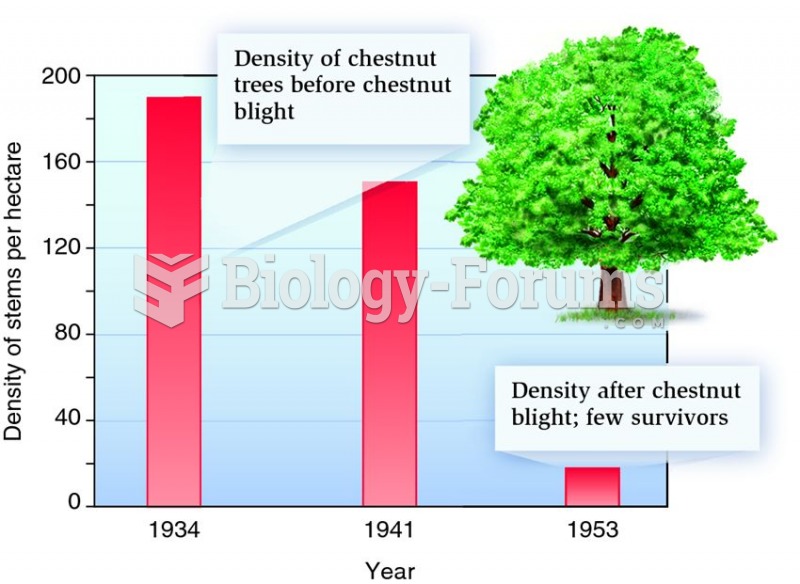
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.