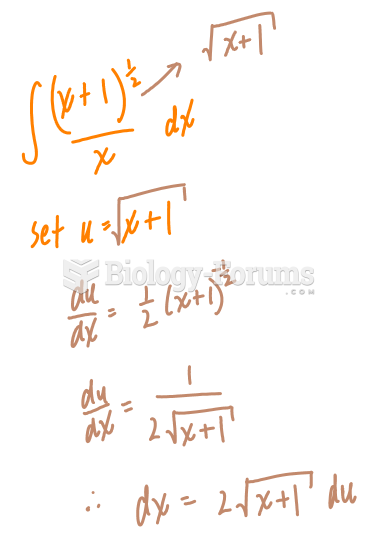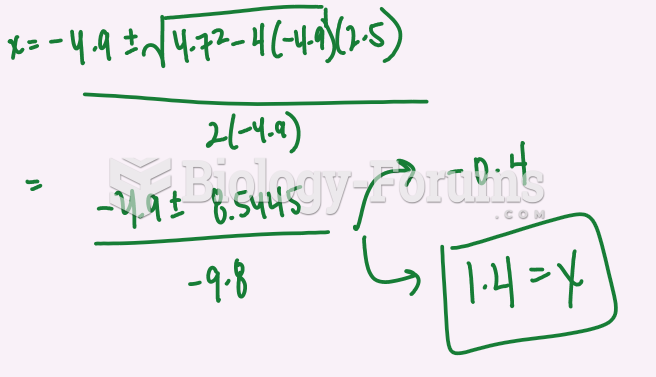Answer to Question 1
Various examples of hazards and solutions can be provided
Microorganism Issues- Some examples can include:
Powdery Mildew: Grape vines infected with powdery mildew display white powder-like patches on leaves, stems and grapes. Powdery mildew can grow well in both wet and dry regions. It can kill leaves and defoliate the vine. Grape quality suffers when leaves are unable to perform proper photosynthesis.
Downey Mildew: Symptoms include light green to yellow spots scattered across the leaf. These spots appear greasy and are commonly referred to as oil spots. The biggest concern for downey mildew is leaf infection.
Black Rot: Symptoms include brown circular lesions on infected leaves. Left untreated it can destroy an entire grape crop. The biggest concern for black rot is the infection of young grape clusters. Infected berries first appear light brown and then turn to near black masses develop on the surface.
Bunch Rot: Infected berries appear soft and watery. In high humidity regions berries become covered in a grayish growth of fungus. Tight-clustered grape varieties are most vulnerable to bunch rot.
Out of the possible solutions to the vineyard challenge of microorganismscanop y management is considered one of the most effective solutions. Promoting good air circulation, sunlight penetration, and uniform leaf development are all benefits of practicing proper canopy management.
Animals/Pest Issues - Some examples can include:
Phylloxera (fil-LOX-er-uh) The most feared enemy of grapevines is a small plant louse Phylloxera vastatrix. This aphid feeds on the roots of grapevines (especially on the highly vulnerable Vinifera rootstock species), causing the vine to starve and thus preventing fruit development. The solution was to graft Vinifera vines to the American rootstock (which was much more resistant to Phylloxera).
Weather Issues - Some examples can include:
Wind may prevent pollination of the flowers during the early part of the season. Later in the season, the winds can knock fruit off the vine and heavier winds can knock vines over. Some of the heaviest winds occur in Southern France (the Mistral) where they have been known to rip vines right out of the ground.
Frost is a serious danger in many vineyards, especially those located on the valley floors where the coldest air settles on frosty nights. Frost will kill green tissues on vines. Late spring frost can cause bud damage
and may affect the yield by producing fewer grape clusters. A freeze on the other hand can kill dormant life. An early fall freeze can be devastating. In some colder regions grape growers actually remove the vines from the trellis and bury them just below the surface so they will survive the winter.
Sprayers, burners, and wind machines can all be used collectively or separately where frost is a constant danger to the buds, flowers, or berries. Wind machines are used to distribute heat from a central heat source, such as a fire or chaufferettes (gas heaters), that warms the grapes (or vines) to keep them free of frost. Many grape growers located in cold climates may also use aspersion, which involves sprayers that release water into the air. The water that lands on the grapes (or buds) forms an outer ice shell, but a warm, protected state is maintained on the inside.
Rains are a concern both in early spring and at harvest time. Too much rain can prevent pollination of flowers in the spring. If it rains near harvest time, the fruit may be oversaturated and the flavors, sugars, and acid that have been developing throughout the growing season may be diluted.
Answer to Question 2
The server should select a type of clothing that projects a professional image.