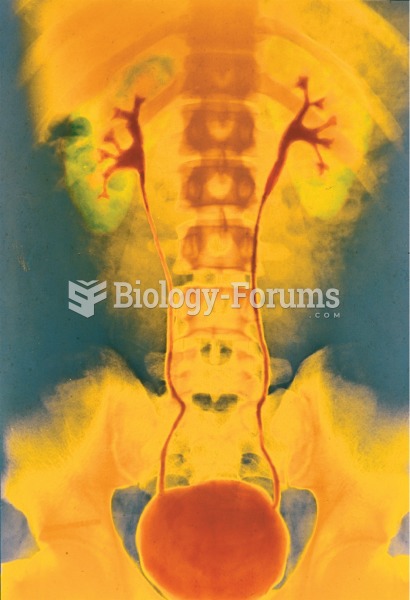
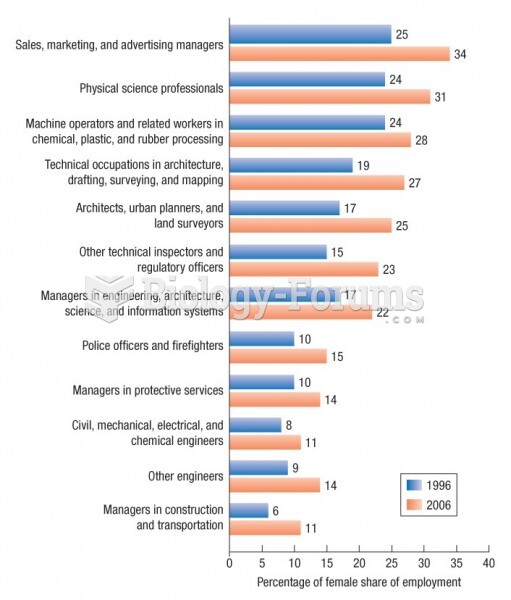
Answer to Question 1
Defense Attorney
The defense attorney helps to clarify jurisdictional problems and to decide whether there is sufficient evidence to warrant filing a formal petition. The defense attorney helps outline the child's position regarding detention hearings and bail and explores the opportunities for informal adjustment of the case. If no adjustment or diversion occurs, the defense attorney represents the child at adjudication, presenting evidence and cross-examining witnesses to see that the child's position is made clear to the court. Defense attorneys also play a critical role in the disposition hearing. They present evidence bearing on the treatment decision and help the court formulate alternative plans for the child's care. Finally, defense attorneys pursue any appeals from the trial, represent the child in probation revocation proceedings, and generally protect the child's right to treatment.
Guardian ad litem
The guardian ad litemordinarily seen in abuse, neglect, and dependency casesmay be appointed in delinquency cases when there is a question of a need for a particular treatment (e.g., placement in a mental health center) and offenders and their attorneys resist placement. The guardian ad litem may advocate for the commitment on the ground that it is in the child's best interests. The guardian ad litem fulfills many roles, ranging from legal advocate to concerned individual who works with parents and human service professionals in developing a proper treatment plan that best serves the interests of the minor child.
Juvenile Prosecutor
The juvenile prosecutor is the attorney responsible for bringing the state's case against the accused juvenile. The prosecutor has the power either to initiate or to discontinue delinquency or status-offense allegations. Like police officers, prosecutors have broad discretion in the exercise of their duties. Because due process rights have been extended to juveniles, the prosecutor's role in the juvenile court has in some ways become similar to the prosecutor's role in the adult court. A number of states have passed legislation giving prosecutors control over intake and waiver decisions.
Juvenile Court Judge
Rule on pretrial motions involving such legal issues as arrest, search and seizure, interrogation, and lineup identification.
Make decisions about the continued detention of children prior to trial.
Make decisions about plea-bargaining agreements and the informal adjustment of juvenile cases.
Handle trials, rule on the appropriateness of conduct, settle questions of evidence and procedure, and guide the questioning of witnesses.
Assume responsibility for holding disposition hearings and deciding on the treatment accorded the child.
Handle waiver proceedings.
Handle appeals where allowed by statute.
Answer to Question 2
T