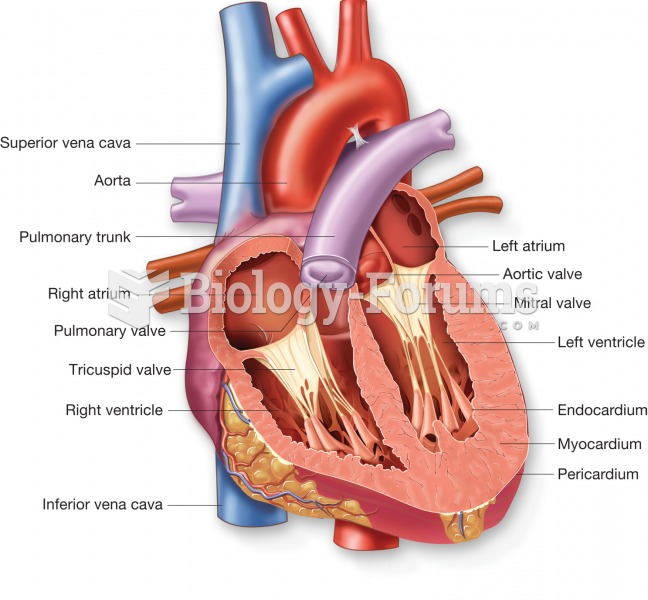
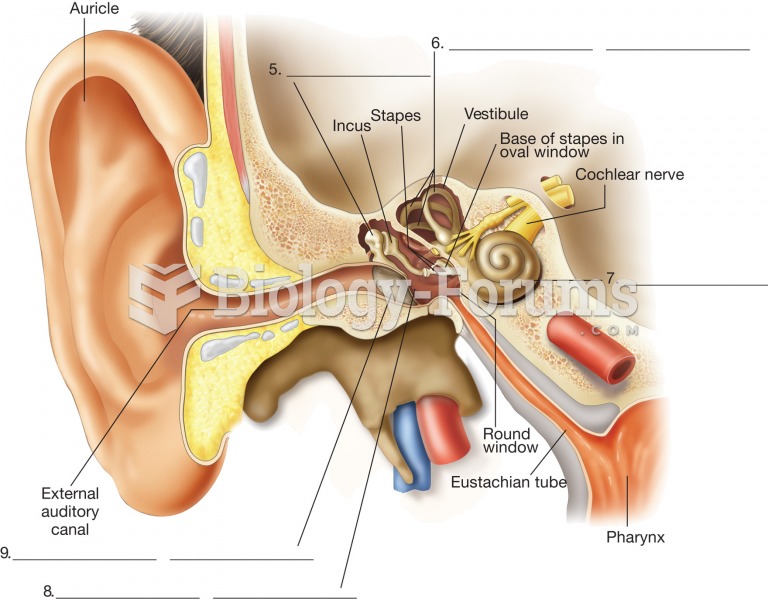
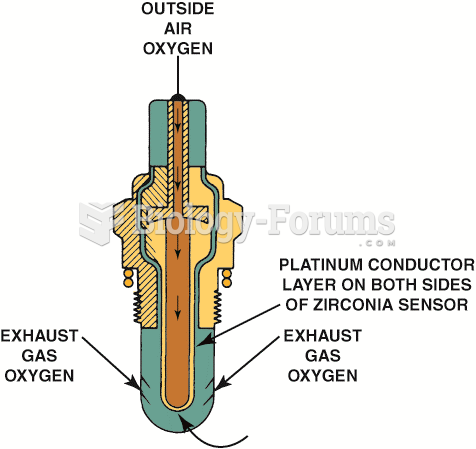
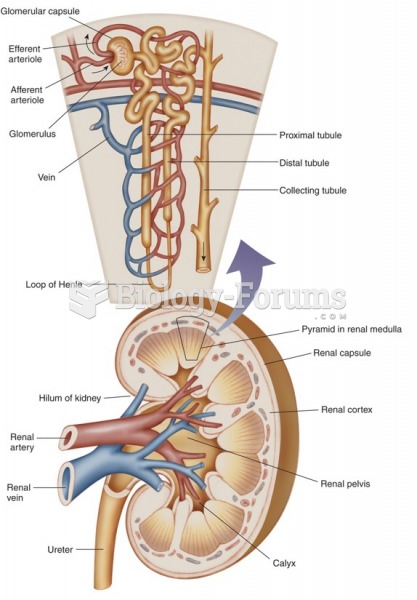
Answer to Question 1
A harm reduction approach involves lessening the harms caused to youths by drug use and by some of the more punitive responses to drug use. Harm reduction encapsulates some of the efforts advanced under the community and treatment strategies noted above, but maintains as its primary focus efforts to minimize the harmful effects of drug use. This approach includes the following components:
The availability of drug treatment facilities so that all addicts who wish to do so can overcome their habits and lead drug-free lives.
The use of health professionals to administer drugs to addicts as part of a treatment and detoxification program.
Needle exchange programs that will slow the transmission of HIV and educate drug users about how HIV is contracted and spread.
Special drug courts or pretrial diversion programs that compel drug treatment.
Needle exchange programsproviding drug users with clean needles in exchange for used oneshave been shown to maintain the low prevalence of HIV transmission among drug users and lower rates of hepatitis C. Methadone maintenance clinics in which heroin users receive doctor-prescribed methadone (a nonaddictive substance that satisfies the cravings caused by heroin) have been shown to reduce illegal heroin use and criminal activity.
Student views will vary.
Answer to Question 2
One approach to drug control is to deter the sale of drugs through apprehension of large-volume drug dealers, coupled with enforcement of drug laws that carry heavy penalties. This approach is designed to punish known dealers and users and to deter those who are considering entering the drug trade.
A major effort has been made to cut off supplies of drugs by destroying overseas crops and arresting members of drug cartels; this approach is known as source control.
The federal government has been encouraging exporting nations to step up efforts to destroy drug crops and to prosecute dealers. Other less aggressive source control approaches, such as crop substitution and alternative development programs for the largely poor farmers in other countries, have also been tried, and a review of international efforts suggests that some success can be achieved in reduction of narcotic crop production..
Three South American nationsPeru, Bolivia, and Colombiahave agreed to coordinate control efforts with the United States.
Even when efforts are successful in one area, they may result in a shift in production to another area or in the targeted crop being replaced by another.
For example, enforcement efforts in Peru and Bolivia were so successful that they altered cocaine cultivation patterns. As a consequence, Colombia became the premier coca-cultivating country when the local drug cartels encouraged growers to cultivate coca plants.
When the Colombian government mounted an effective eradication campaign in the traditional growing areas, the cartel linked up with rebel groups in remote parts of the country for their drug supply.
Student views will vary.