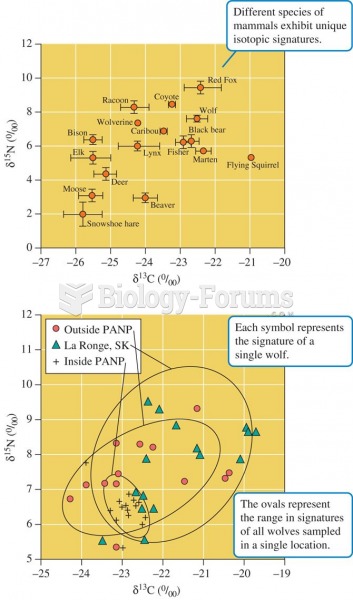
|
|
|
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.
Colchicine is a highly poisonous alkaloid originally extracted from a type of saffron plant that is used mainly to treat gout.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
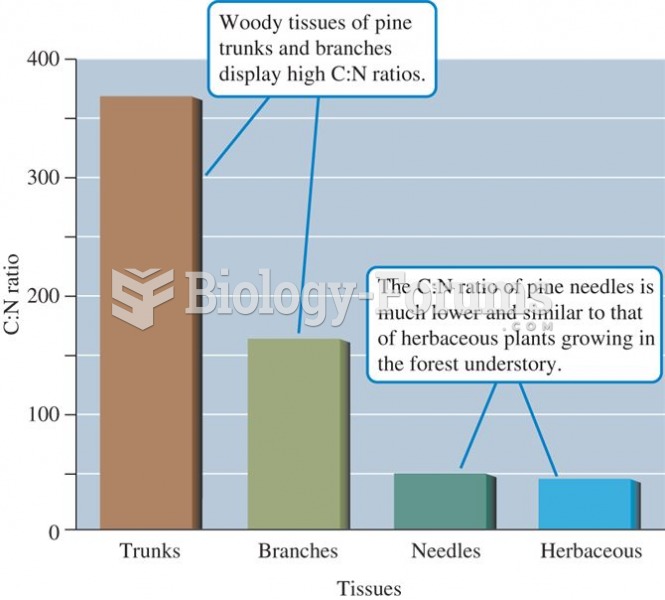 C:N ratios differ a great deal among the tissues of pines and between the woody tissues of pines and
C:N ratios differ a great deal among the tissues of pines and between the woody tissues of pines and
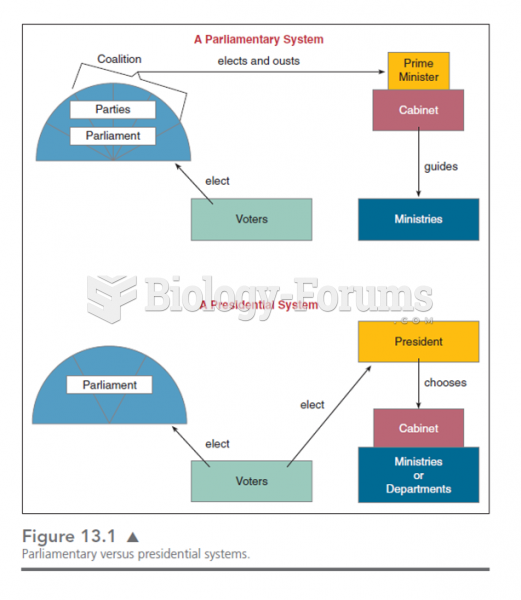 This chart shows the various lines of responsibility and how they differ in presidential and parliam
This chart shows the various lines of responsibility and how they differ in presidential and parliam