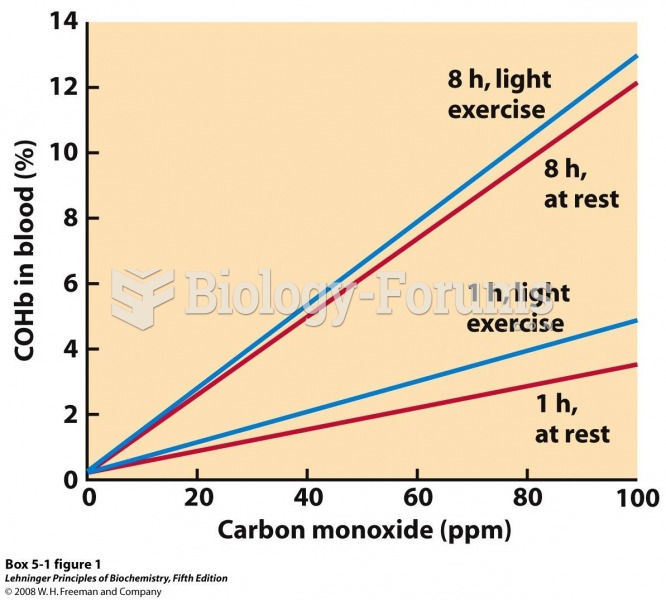
Answer to Question 1
The Fourth Amendment contains two basic clauses: The reasonableness clause, which proscribes unreasonable searches and seizures, followed by the warrant clause, which says that no Warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by Oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized.
Some have argued that the warrant clause gives meaning to the reasonableness clause, so that any search conducted without a warrant is deemed unreasonable, and therefore unconstitutional. Justice Frankfurter took this position in United States v. Rabinowitz, 339 U.S. 56 (1950): What is the test of reason which makes a search reasonable?There must be a warrant to permit search, barring only inherent limitations upon that requirement when there is a good excuse for not getting a search warrant. This is the warrant requirement interpretation, which prefers that a neutral magistrate come between the officer conducting the search and the citizen targeted by the search.
Others have argued that the reasonableness clause and the warrant clause should be read separately. Their position is that the reasonableness of a search should not depend on whether a warrant was obtained or on whether there was a good excuse for not obtaining a warrant. Instead, they believe that the courts should focus on the factual circumstances justifying the search. They also believe, specifically, that the courts should consider the manner in which the search was executed, not whether a warrant was secured. The main protection offered by the Fourth Amendment should lie, then, not with a judge prior to the search but with the courts after the search. In this view, the courts should reflect on what occurred and seek to determine whether the search was reasonable at the time it was actually conducted.
Answer to Question 2
The fruit of the poisonous tree doctrine is the initial unconstitutional search or seizure. Anything obtained from the tree is considered forbidden fruit that should be excluded.