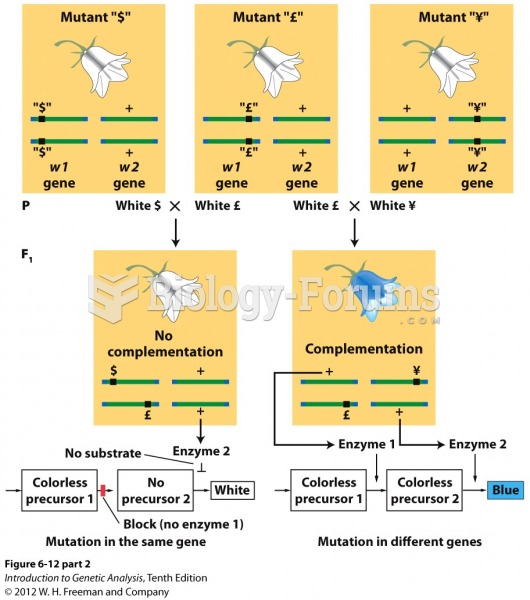
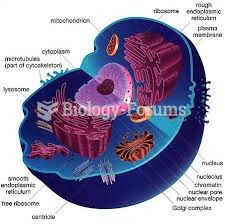
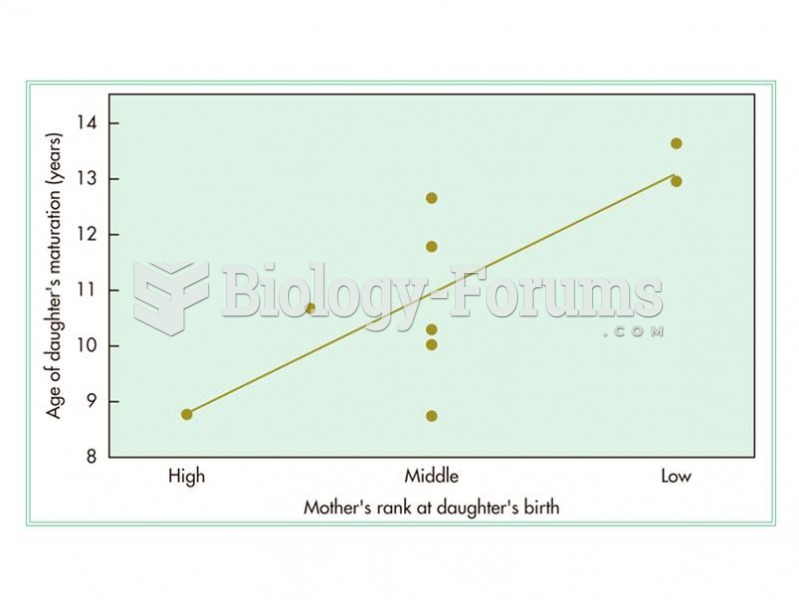
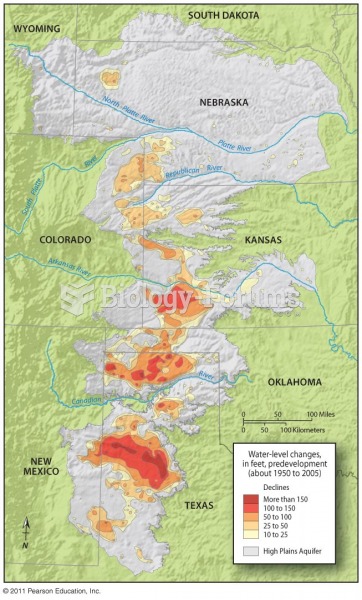
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Did you know?
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.
Did you know?
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Did you know?
All adverse reactions are commonly charted in red ink in the patient's record and usually are noted on the front of the chart. Failure to follow correct documentation procedures may result in malpractice lawsuits.
Did you know?
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.