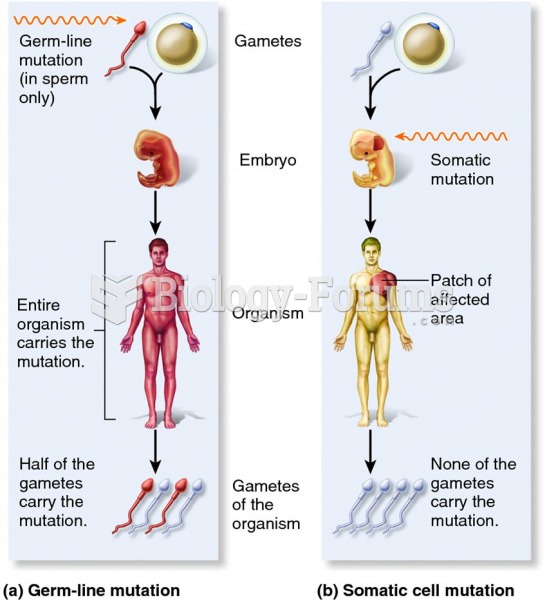
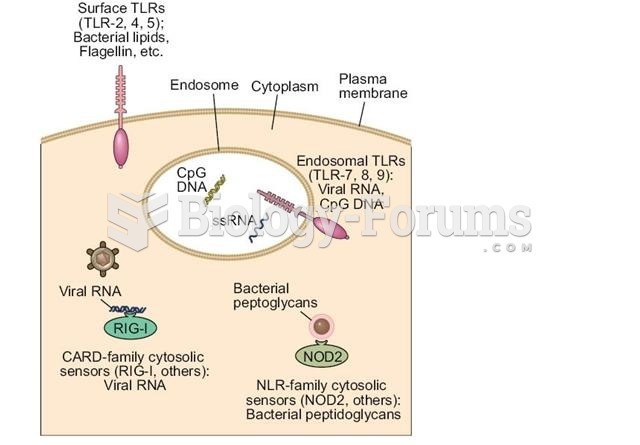
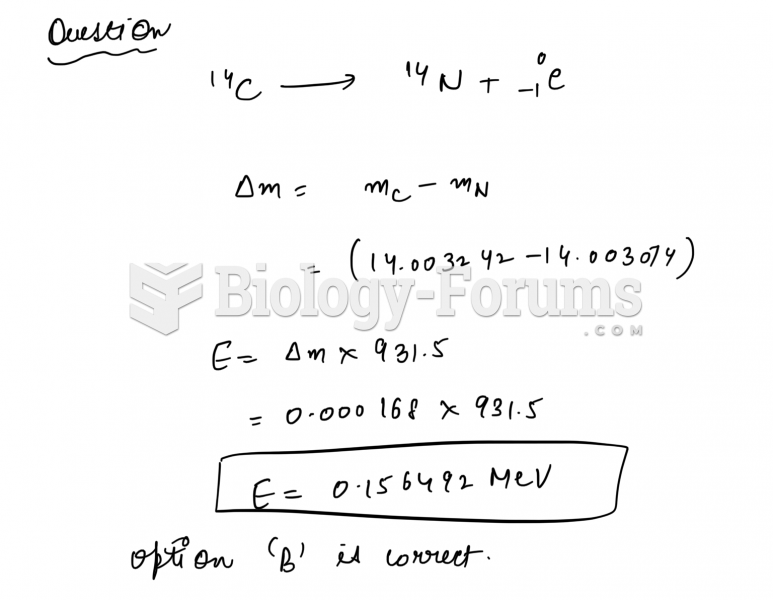
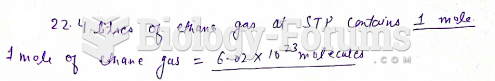|
|
|
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.
Since 1988, the CDC has reported a 99% reduction in bacterial meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, due to the introduction of the vaccine against it.
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.