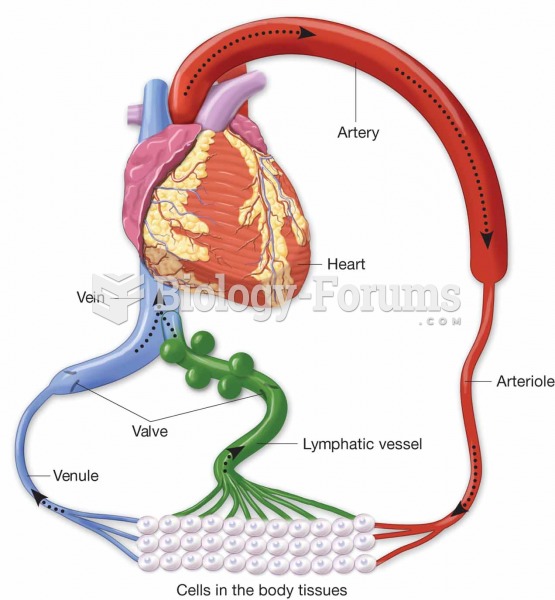
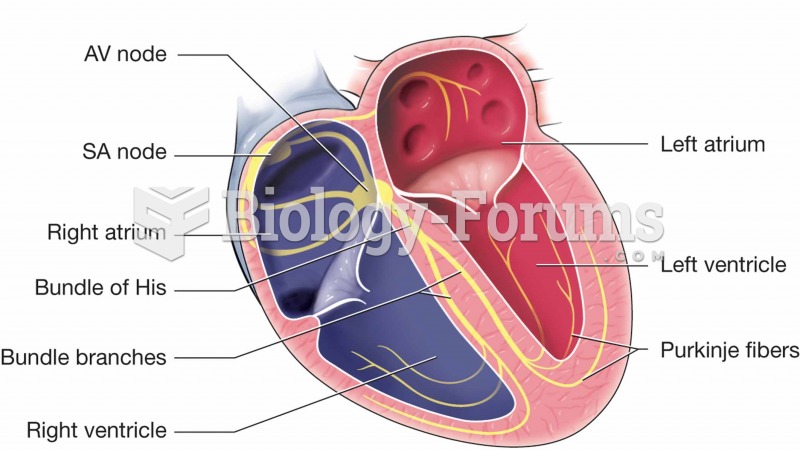
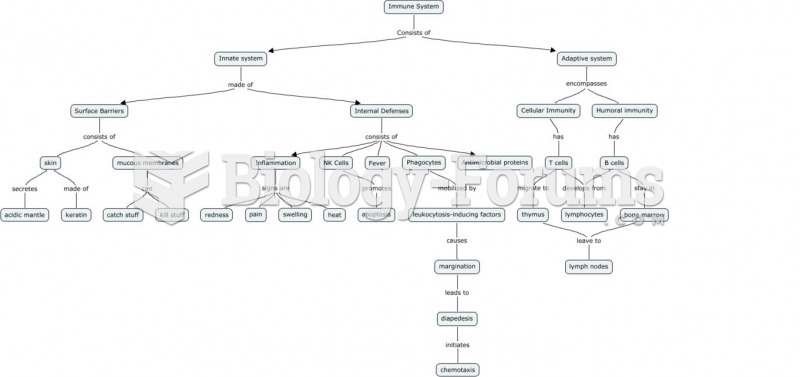
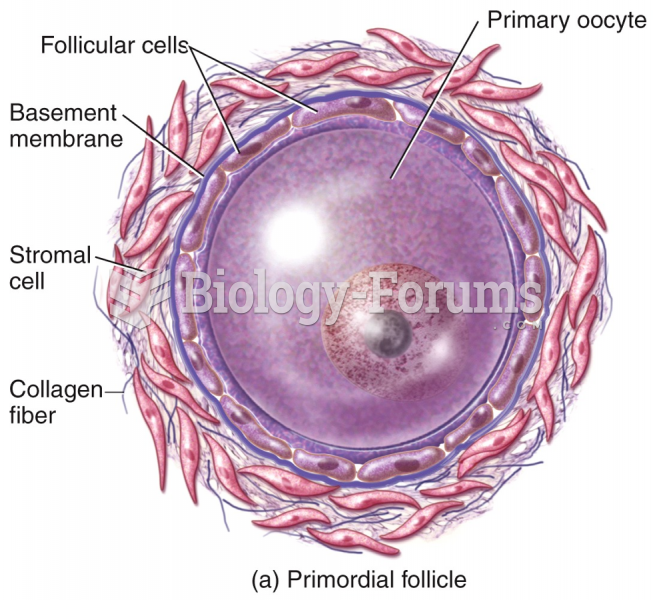
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
Did you know?
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
Did you know?
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Did you know?
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
Did you know?
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.