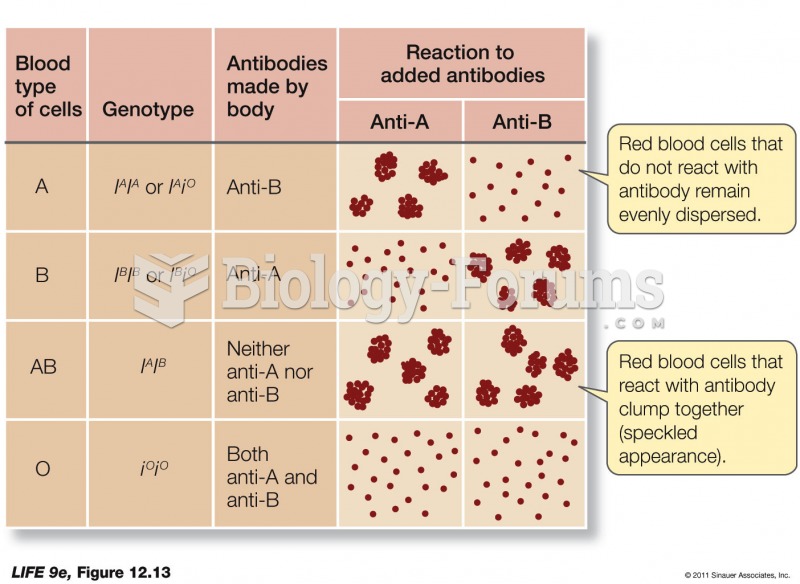
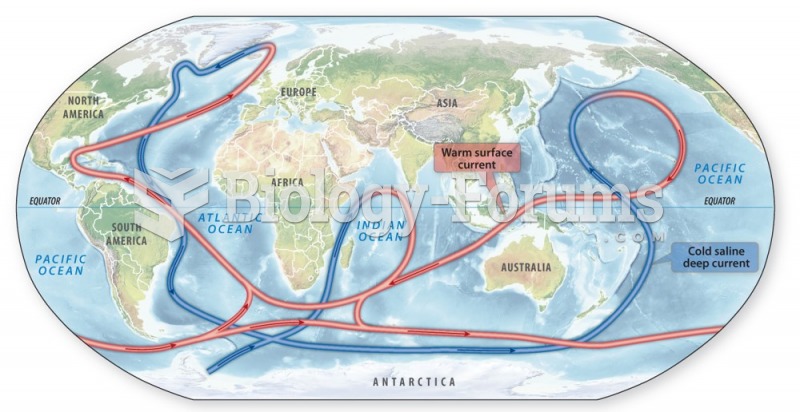
Answer to Question 1When dissolved in water CO2 is present in several different forms: carbonic acid (H2CO3),
the bicarbonate ion (HCO3-), and the carbonate ion (CO32-), including the release of
hydrogen ions (H+) as these constituents breakdown.
Step One: CO2 + H2O <=> H2CO3
Step Two: H2CO3 <=> HCO3- + H+
Step Three: HCO3- + H+ <=> CO32- + 2H+
In Step One, carbon dioxide and water combine to form carbonic acid. Carbonic acid rapidly
dissociates into a bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) and a hydrogen ion (H+) in Step Two. Most of the
CO2 dissolved in seawater ends up as HCO3-. Some of the bicarbonate and hydrogen ions
will then combine to form carbonate (CO32-) ions and two hydrogen ions (2H+) in Step
Three. At any given pH CO2, H2CO3, HCO3-, CO32- and H+ exist in equilibrium with each
other. If acid is added to the system and pH decreases, the reaction proceeds toward Step One
(to the left), raising the pH by removing excess H+ ions. If an alkaline solution is added, and the pH increases, the reaction proceeds toward Step Three (to the right), lowering the pH by
releasing H+ ions.
Answer to Question 2Oxygen is abundant near the surface in the oceans brightly lit upper layer because of the
activity of marine photosynthesizers (plants and plantlike organisms). Since plants and
plantlike organisms require carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, surface CO2 concentrations
tend to be low. A decrease in oxygen below the sunlit upper layer usually results from the
respiration of bacteria and marine animals, as well as, oxygen consumption through the decay
of tiny dead organisms slowly sinking through the area. Because photosynthesis cannot take
place in the dark, CO2 given off by animals and bacteria tends to build up at depths below the
sunlit layer. Levels of CO2 also increase with depth because its solubility increases as
pressure increases and temperature decreases. Oxygen levels are slightly higher in deeper
water because fewer animals are present to take up the oxygen that reaches these depths.