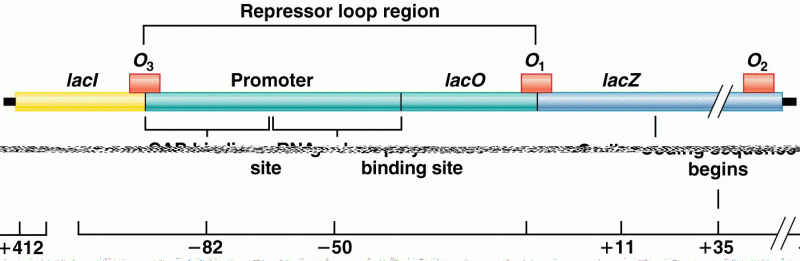
|
|
|
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
About 60% of newborn infants in the United States are jaundiced; that is, they look yellow. Kernicterus is a form of brain damage caused by excessive jaundice. When babies begin to be affected by excessive jaundice and begin to have brain damage, they become excessively lethargic.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.


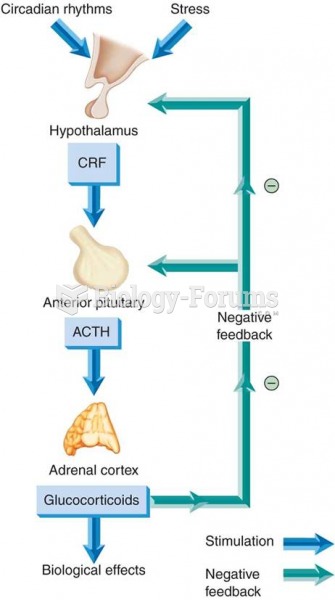
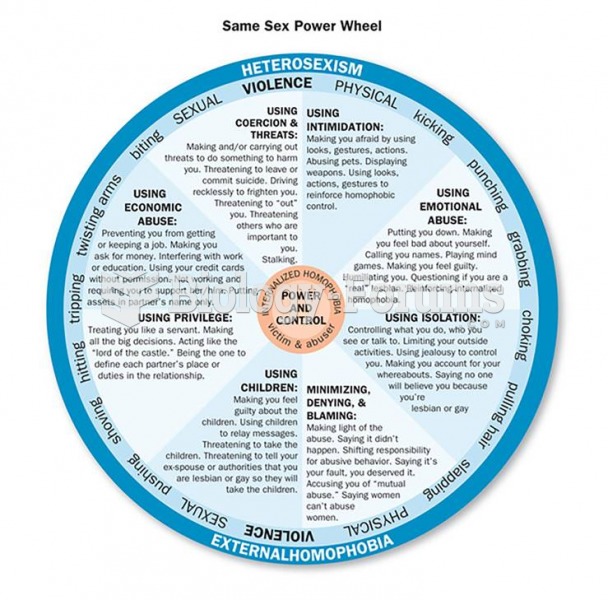
![Chickenpox rash. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC]/Ann Cain)](https://biology-forums.com/gallery/30/medium_548020_08_06_17_10_52_37_306981954.jpeg)