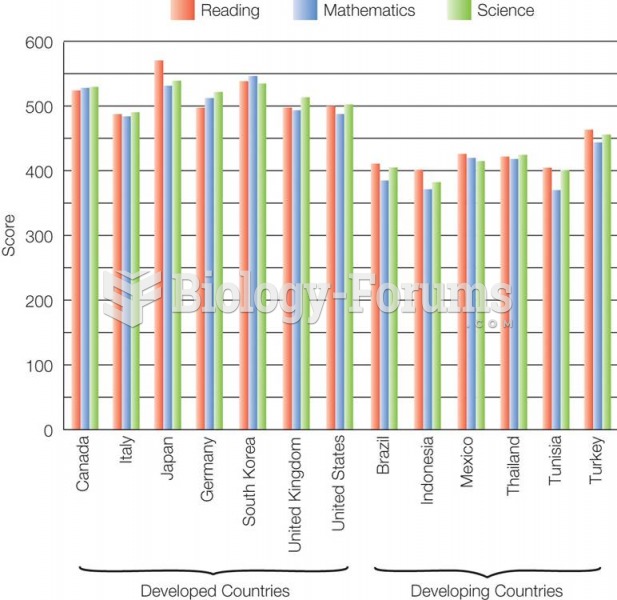
Answer to Question 1
ANSWER:
d
Answer to Question 2
ANSWER:
A. The four theorists discussed in this chapter are Erikson (Psycho-Social Theory), Piaget (Cognitive Development Theory), Vygotsky (Socio-cultural Theory) and Gardner (Multiple Intelligence Theory).
B.
1. Terms associated with Erikson include the 4 stages of psycho-social development that impact early childhood:
Trust versus Mistrust (ages birth to 1)
Autonomy versus Shame and Doubt (second year)
nitiative versus Guilt (3 to 5 years)
Industry vs. Inferiority (6 to 11 years)
2. Terms associated with Piaget include schema, equilibrium, assimilation, accommodation, egocentrism, active exploration and discovery, constructivism, object permanence, and symbolic thinking as well as stages:
Sensorimotor stage (birth to about 2 years)
Preoperational stage (about 2 to 7 years)
Concrete Operations stage (about 7 to 12 years)
Formal Operations stage (12 years through adulthood)
3. Terms associated with Vygotsky include zone of proximal development and scaffolding
4. Terms associated with Howard Gardners Multiple intelligence theory are:
Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence
Logical-Mathematical Intelligence
Musical-Rhythmic Intelligence
Visual-Spatial Intelligence
Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence
Interpersonal Intelligence
Intrapersonal Intelligence
Naturalist Intelligence
C.
1. Eriksons PsychoSocial Theory
The stages of development help us understand the importance of allowing children to play out their feelings in an environment of acceptance. Teachers need to have empathy and respect for children.
2. Piagets Cognitive Development Theory
Each of these stages involves a period of formation and a period of attainment. Each builds on the development of the preceding stage. A careful consideration of Piagets concepts, along with close observation of children, helps teachers provide appropriate environments and experiences, ask appropriate questions, moving from simple to complex and from concrete to abstract.
3. Vygotskys SocialCultural Theory
For teachers of young children, the zone of proximal development may be used to provide a theoretical base from which to understand cooperative learning. In the culture of the classroom, this can translate into small-group instruction in which students work together to solve problems. In addition, the role of the teacher includes both designing an educative environment and collaborating with children by scaffolding their efforts to master new skills. From this perspective, Vygotsky-based teaching is activity centered, since it emphasizes creating opportunities for children to engage in culturally meaningful opportunities with
the guidance of teachers and peers.
4. The Multiple Intelligences Theory
This theory is a useful model for developing a systematic approach to nurturing and teaching children and honoring their individual needs and strengths within a classroom setting. Teachers need to guide students into using their combination of intelligences to help them learn whatever they want to learn, as well as what teachers and society believe they have to learn. Understanding of the intelligences should be linked with a curriculum focused on understanding where children are able to apply what they have learned in new situations