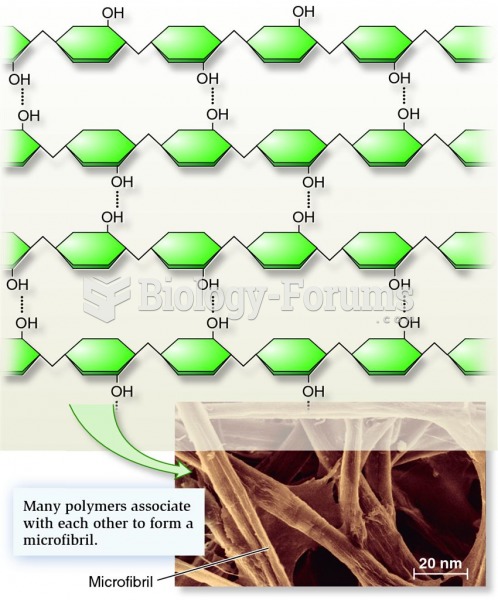
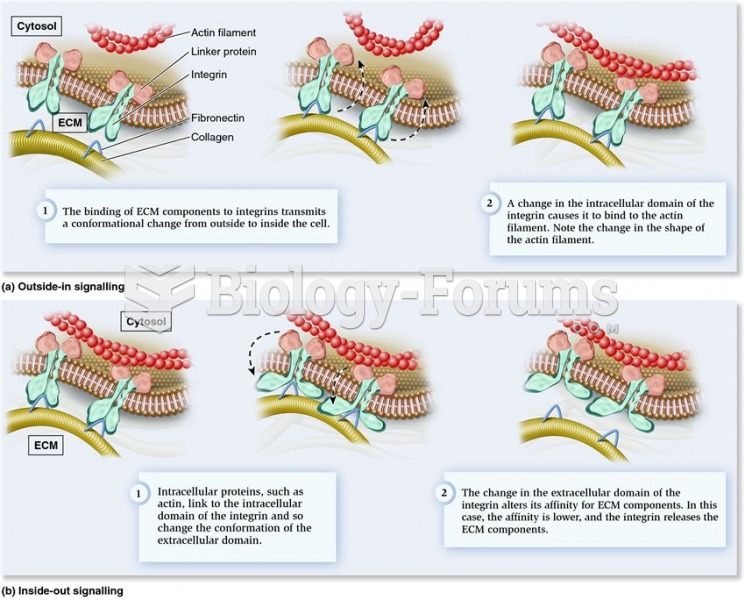
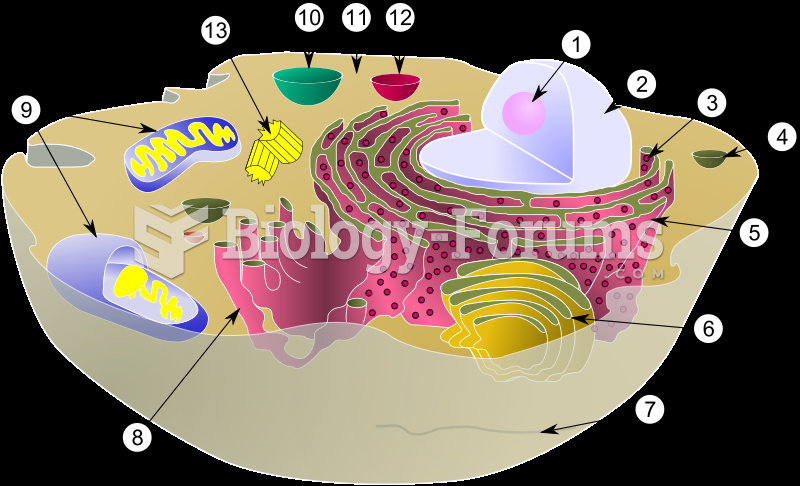
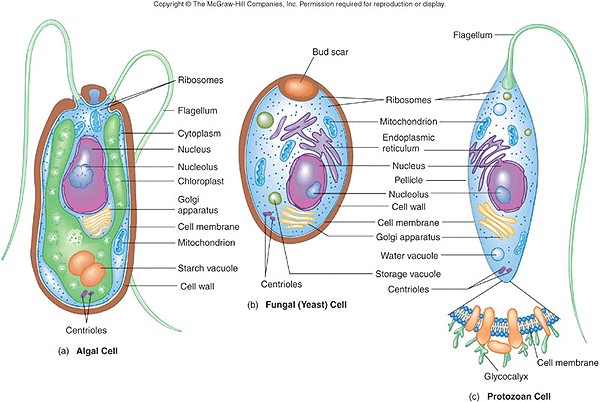
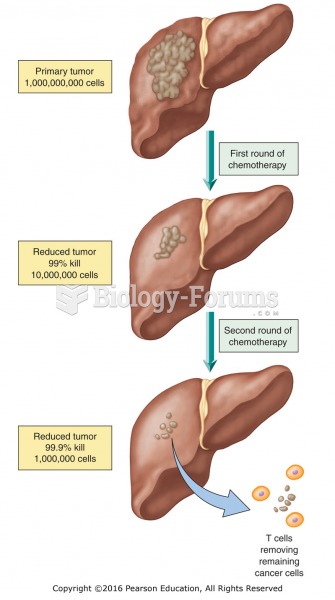
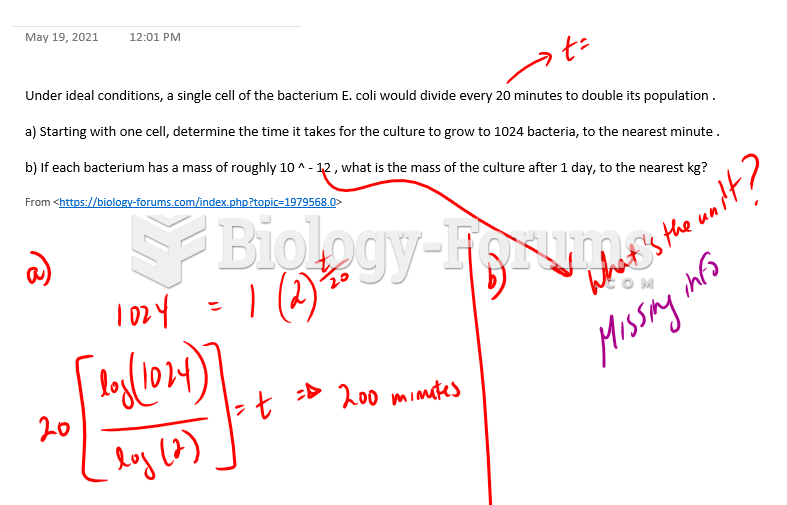
|
|
|
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.