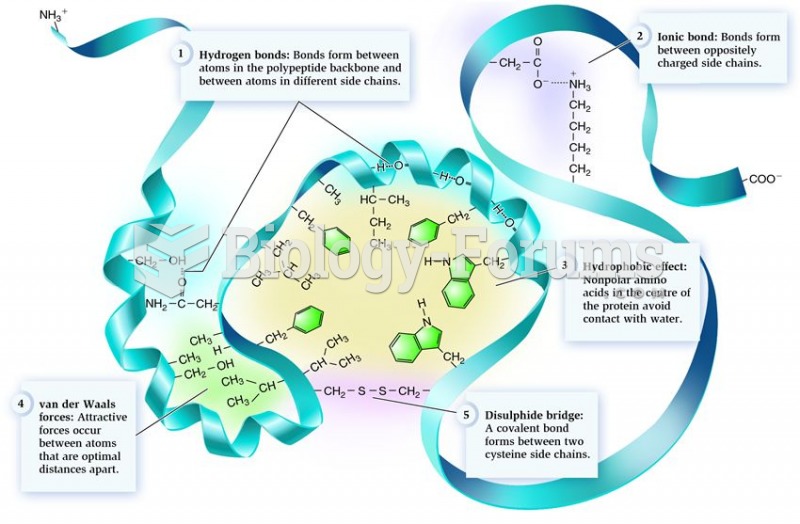
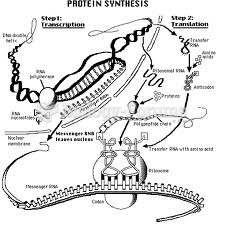
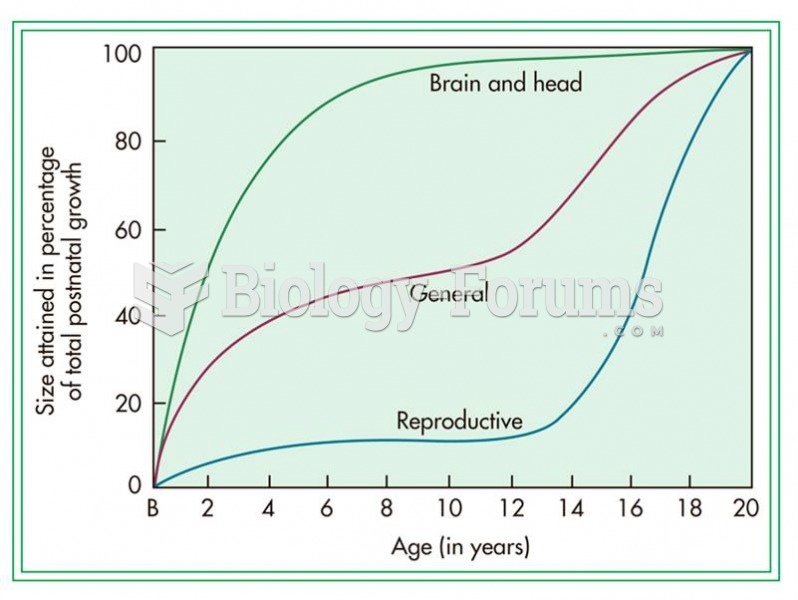
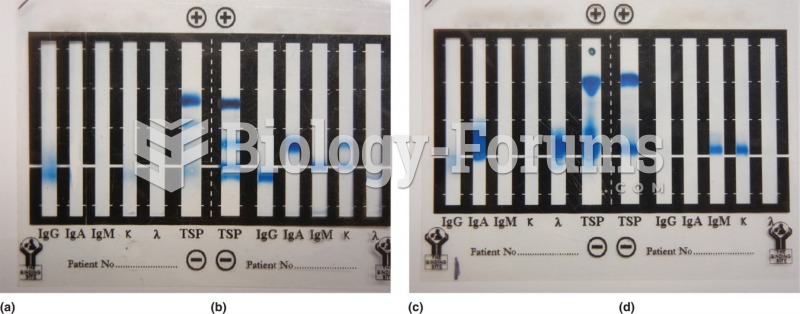
|
|
|
Always store hazardous household chemicals in their original containers out of reach of children. These include bleach, paint, strippers and products containing turpentine, garden chemicals, oven cleaners, fondue fuels, nail polish, and nail polish remover.
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").