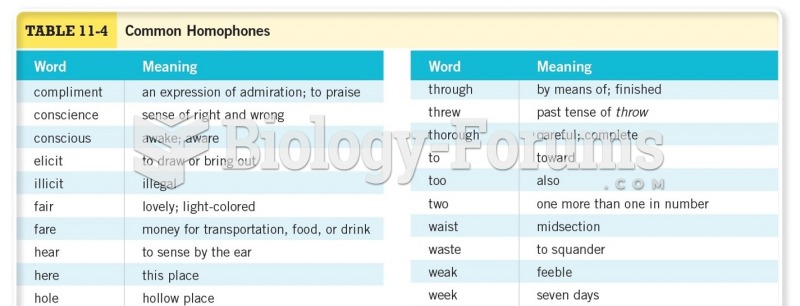
|
|
|
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
All adverse reactions are commonly charted in red ink in the patient's record and usually are noted on the front of the chart. Failure to follow correct documentation procedures may result in malpractice lawsuits.
It is believed that the Incas used anesthesia. Evidence supports the theory that shamans chewed cocoa leaves and drilled holes into the heads of patients (letting evil spirits escape), spitting into the wounds they made. The mixture of cocaine, saliva, and resin numbed the site enough to allow hours of drilling.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
Walt Disney helped combat malaria by making an animated film in 1943 called The Winged Scourge. This short film starred the seven dwarfs and taught children that mosquitos transmit malaria, which is a very bad disease. It advocated the killing of mosquitos to stop the disease.
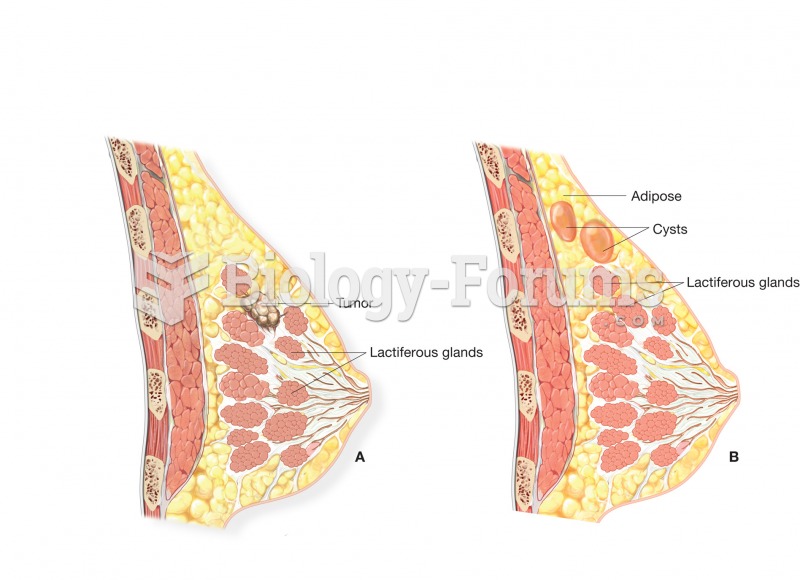 Comparison of breast cancer and fibrocystic disease. (A) Breast with a malignant tumor growing in th
Comparison of breast cancer and fibrocystic disease. (A) Breast with a malignant tumor growing in th
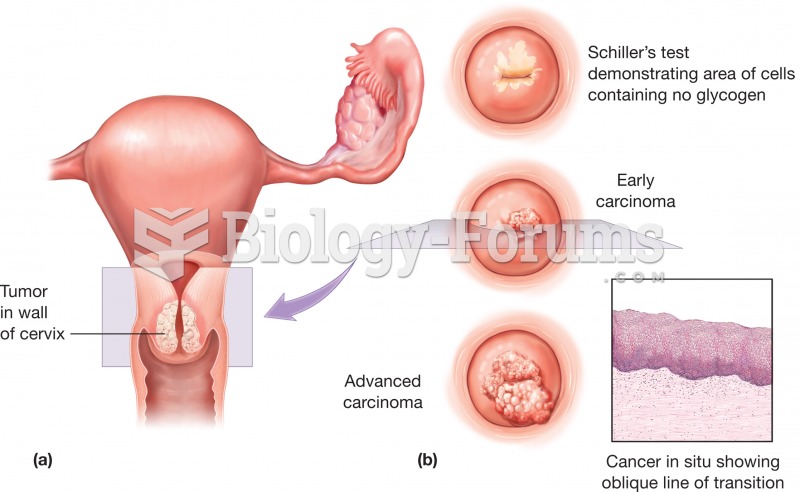 Cervical cancer (a) Top view of the uterus showing the presence of a tumor in the wall of the cervix
Cervical cancer (a) Top view of the uterus showing the presence of a tumor in the wall of the cervix