|
|
|
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
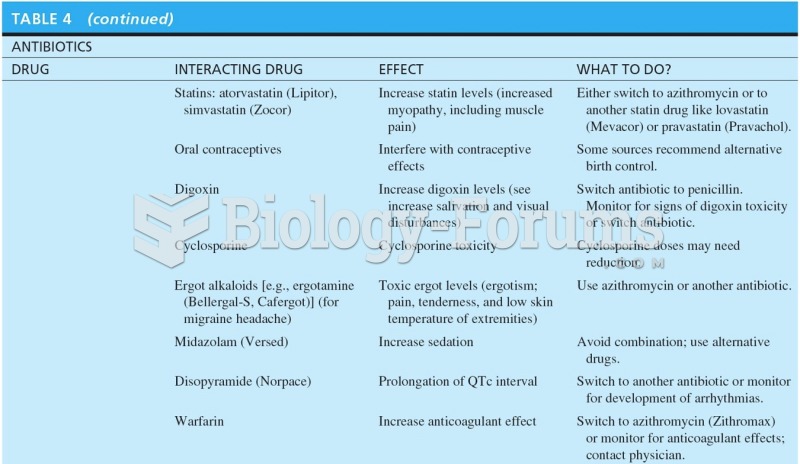
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.
About 80% of major fungal systemic infections are due to Candida albicans. Another form, Candida peritonitis, occurs most often in postoperative patients. A rare disease, Candida meningitis, may follow leukemia, kidney transplant, other immunosuppressed factors, or when suffering from Candida septicemia.