|
|
|
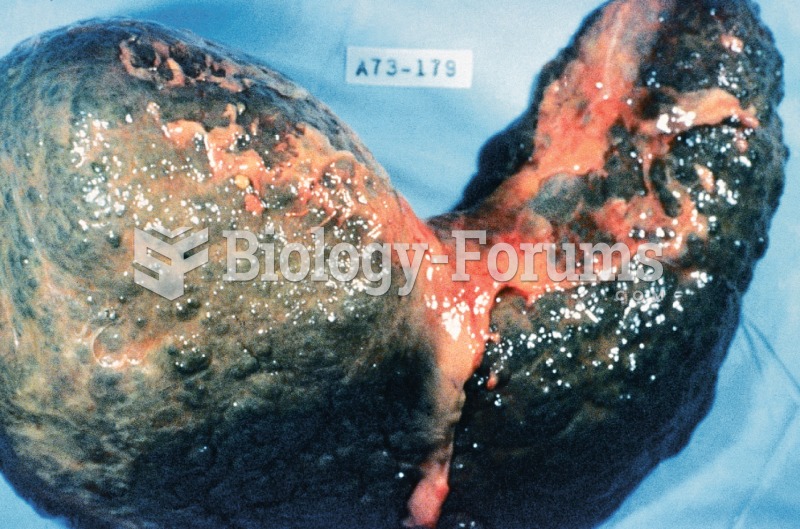
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.