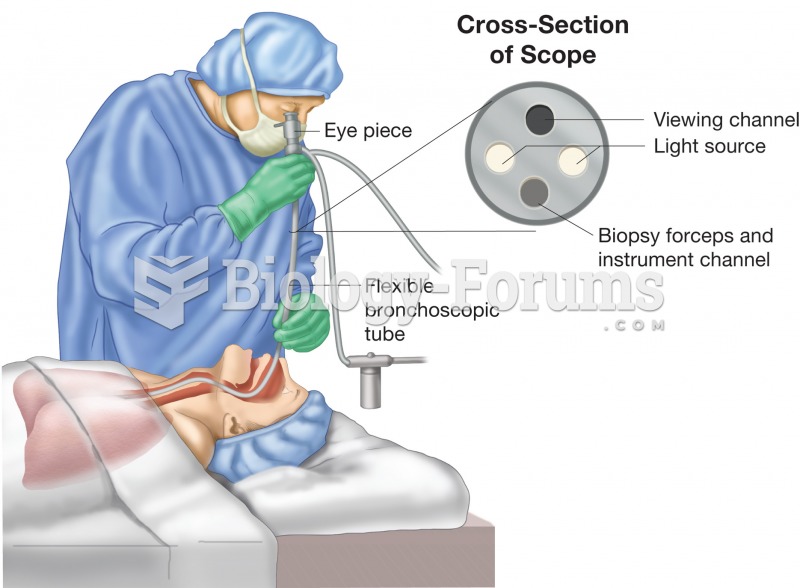
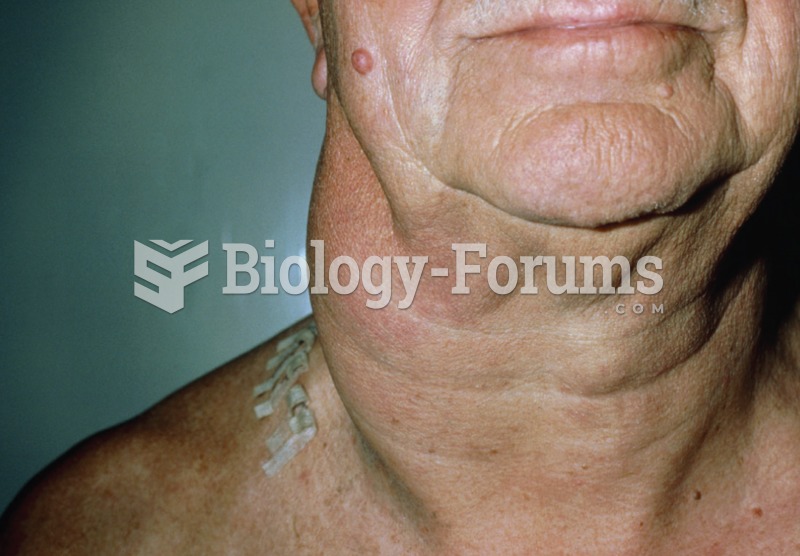
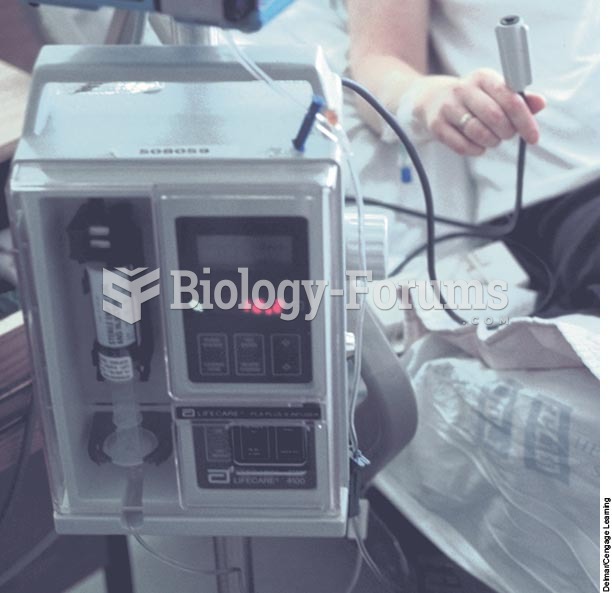
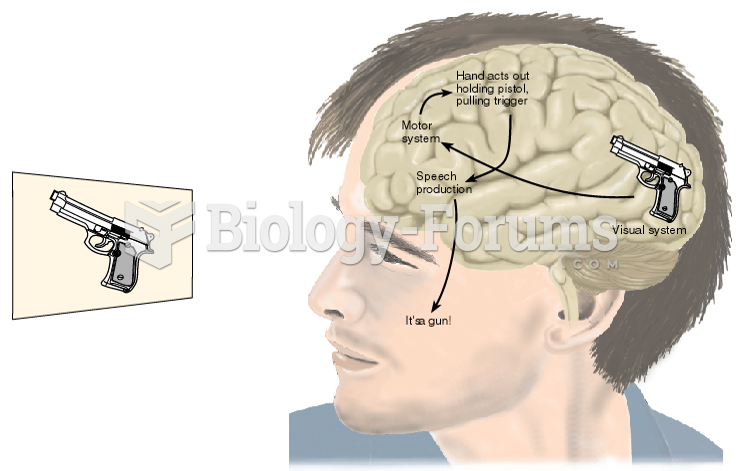
|
|
|
Oliver Wendell Holmes is credited with introducing the words "anesthesia" and "anesthetic" into the English language in 1846.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
About 600,000 particles of skin are shed every hour by each human. If you live to age 70 years, you have shed 105 pounds of dead skin.