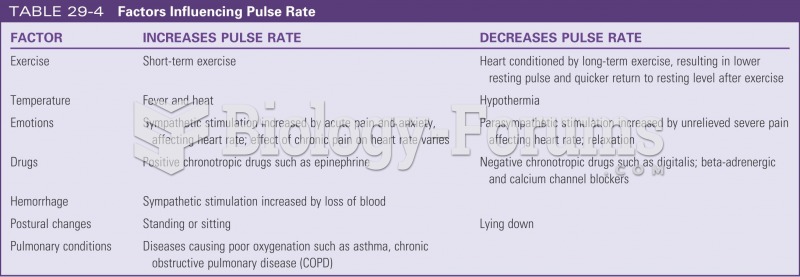
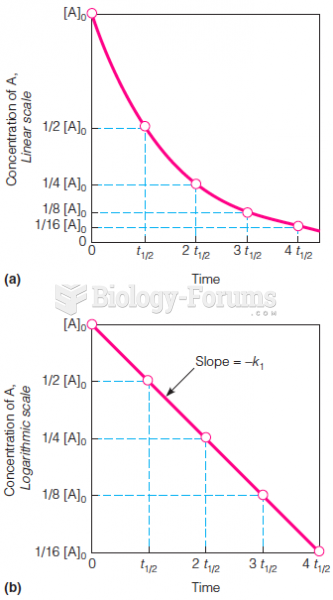
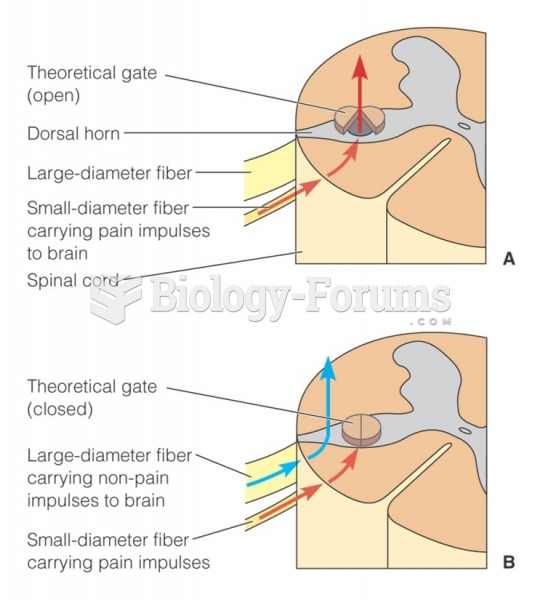
|
|
|
A cataract is a clouding of the eyes' natural lens. As we age, some clouding of the lens may occur. The first sign of a cataract is usually blurry vision. Although glasses and other visual aids may at first help a person with cataracts, surgery may become inevitable. Cataract surgery is very successful in restoring vision, and it is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
As many as 20% of Americans have been infected by the fungus known as Histoplasmosis. While most people are asymptomatic or only have slight symptoms, infection can progress to a rapid and potentially fatal superinfection.