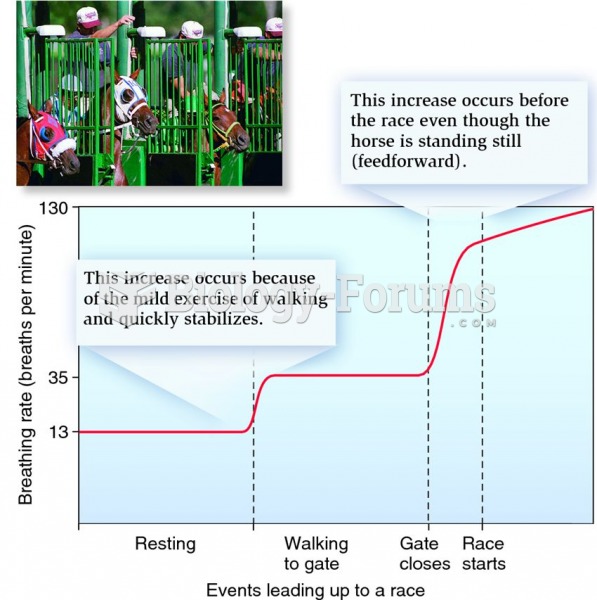
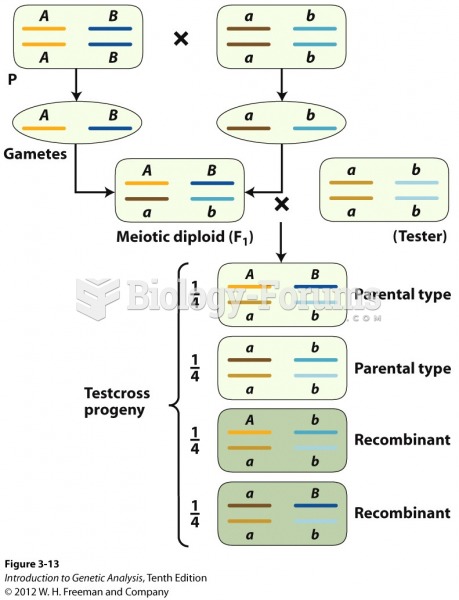
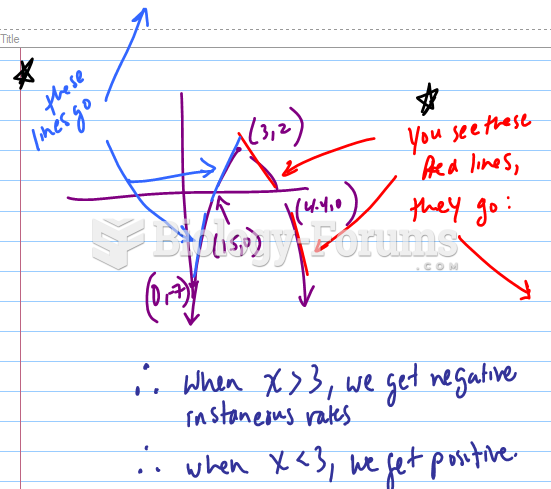
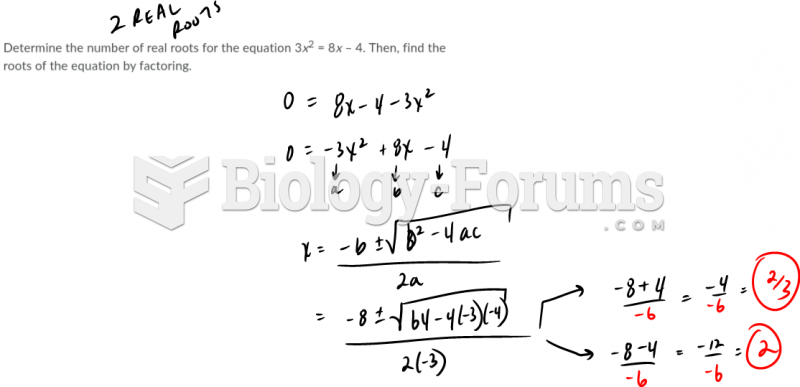
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
Did you know?
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.