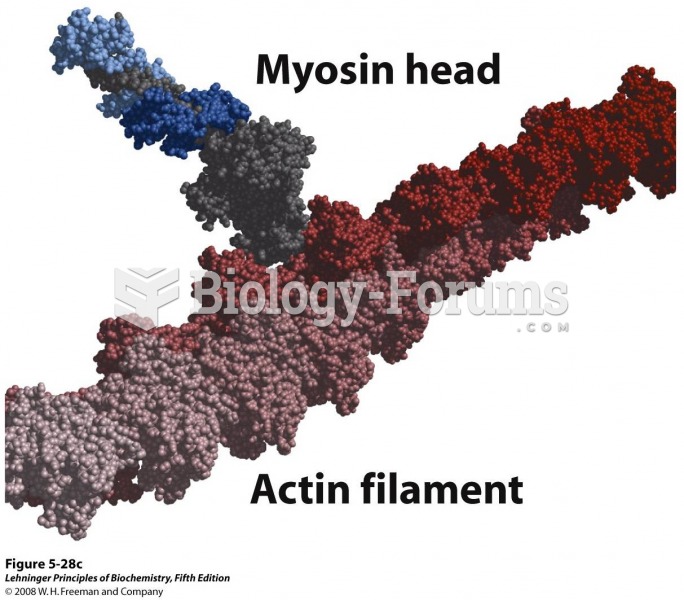
|
|
|
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates's recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."