|
|
|
Cocaine was isolated in 1860 and first used as a local anesthetic in 1884. Its first clinical use was by Sigmund Freud to wean a patient from morphine addiction. The fictional character Sherlock Holmes was supposed to be addicted to cocaine by injection.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
Astigmatism is the most common vision problem. It may accompany nearsightedness or farsightedness. It is usually caused by an irregularly shaped cornea, but sometimes it is the result of an irregularly shaped lens. Either type can be corrected by eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
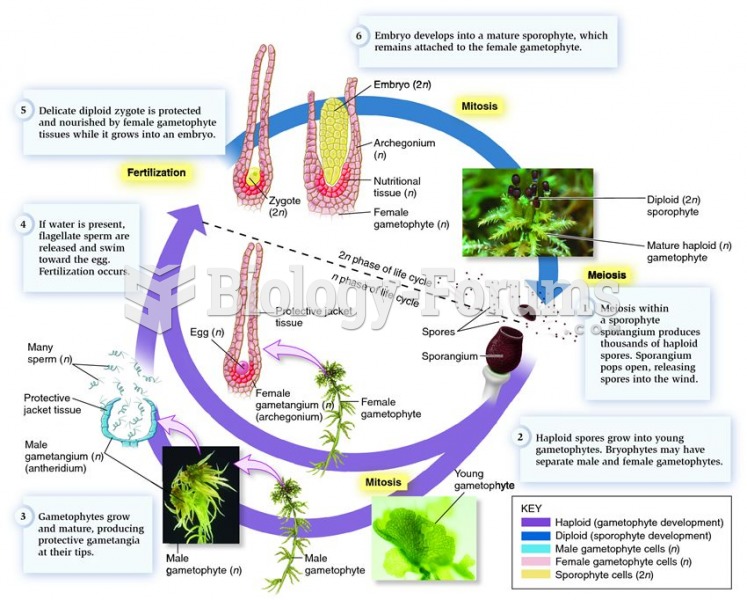 The life cycle of the early diverging moss genus, Sphagnum, illustrating reproductive adaptations th
The life cycle of the early diverging moss genus, Sphagnum, illustrating reproductive adaptations th
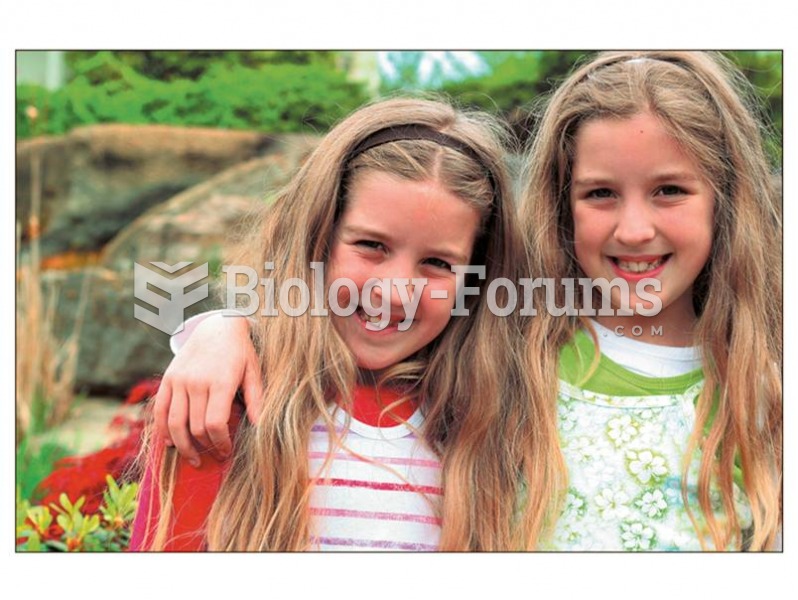 The twin method can be used to investigate genetic and environmental influences on the development o
The twin method can be used to investigate genetic and environmental influences on the development o