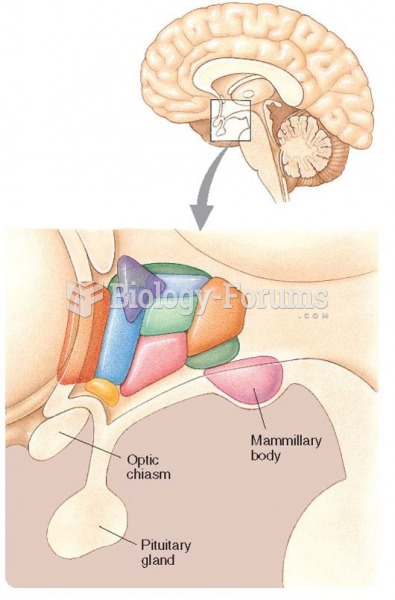
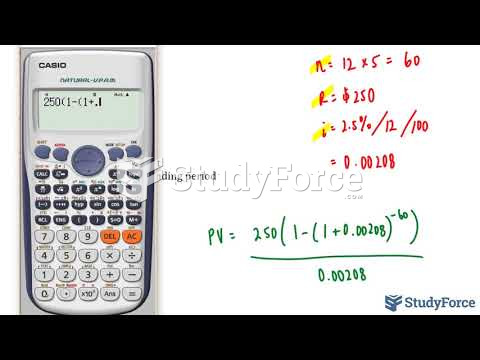
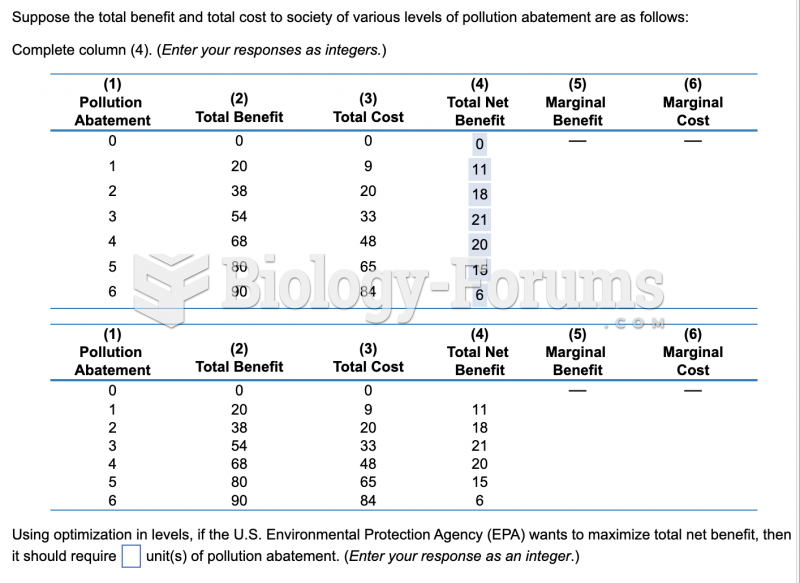
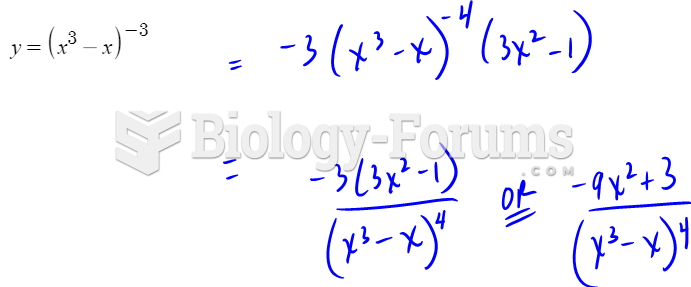Answer to Question 1
Grouping employees into a team structure does not mean that they will automatically function as a team. A group must go through a developmental process to begin to function as a team. Members need training in such areas as problem solving, goal setting, and conflict resolution. Teams must be encouraged to establish the three Rs-roles, rules, and relationships.
A self-directed work team can become the basic organizational building block to best ensure success in dynamic global competition. Skills for successful participation in team environments are somewhat different from those necessary for success in old-style organizations. Today successful business communicators and team members must possess the ability to:
a. give and take constructive criticism, actively listen, clearly impart one's views to others, and provide meaningful feedback;
b. break down emotional barriers, such as insecurity or condescension;
c. promote team functioning by removing process barriers, such as rigid policies and procedures;
d. understand the feelings and needs of coworkers so members feel comfortable stating their opinions and discussing the strengths and weaknesses of the team;
e. overcome cultural barriers, such as stereotyped roles and responsibilities, that can separate workers from management; and
f. apply leadership skills in a dynamic group setting that results in team success. In dynamic team leadership, referred to as distributed leadership, the role of leader can alternate among members, and more than one leadership style can be active at any given time.
Gender, cultural, and age differences among members of a team can present barriers to team communication. Knowing what behaviors can limit the group process is imperative to maximizing results. Team members might need awareness training to assist in recognizing behaviors that may hinder team performance and in overcoming barriers that can limit the effectiveness of their communication.
Answer to Question 2
Electronic tools create opportunities that range from new kinds of communications to improved quality of messages themselves. Electronic tools, such as the Internet, intranets, document production software, multimedia presentations, Web publishing tools, and email, can help people in various ways, such as by (i) collecting and analyzing data, (ii) shaping messages to be clearer and more effective, and (iii) communicating quickly and efficiently with others in geographically dispersed locations.
Using various communication technologies, individuals can often work in their homes or other remote locations and send and receive work from a company office electronically. Telecommuting offers various advantages, including reduced travel time and increased work flexibility. Laptops and smartphones provide computing power and connectivity for professionals wherever they are. While the public Internet is accessible to everyone and offers a wide array of information, organizations are establishing intranets, which can be understood as a private analog of the Internet, or as a private extension of the Internet confined to a particular organization. An intranet is a computer network that uses Internet Protocol technology to share information, operational systems, or computing services within an organization. Increasingly, intranets are being used to deliver tools or sophisticated corporate directories, sales and customer relationship management tools, project management and so forth, to advance productivity.
Intranets are also being used as corporate culture-change platforms. For example, large numbers of employees discussing key issues in an intranet forum application could lead to new ideas in management, productivity, quality, and other corporate issues. When part of an intranet is made accessible to customers and others outside the business, that segment becomes part of an extranet, or a network between organizations.
A related development is the growing use of social media in organizations. Social media is a group of Internet-based applications that build on the ideological and technological foundations of Web 2.0, and that allow the creation and exchange of user-generated content. Social media depends on mobile and web-based technologies to create highly interactive platforms through which individuals and communities share, co-create, discuss, and modify user-generated content. It introduces substantial and pervasive changes to communication between organizations, communities, and individuals. In a business context, social media provides opportunities to engage in marketing research, communication, sales promotions/discounts, and relationship development/loyalty programs.
Although many benefits are provided through the use of technology in organizations, challenges or risks also must be recognized. The experience can also be expensive in terms of human time spent and charges incurred for online time. Locating information from electronic sources requires that you know the search procedures and methods for constructing an effective search strategy. There are also possible legal liabilities that can arise from improper use of technological resources.
Effective use of various communication technologies helps ensure timely, targeted messages and responses and helps build interpersonal relationships. This responsiveness leads to positive interactions with colleagues and strong customer commitment.