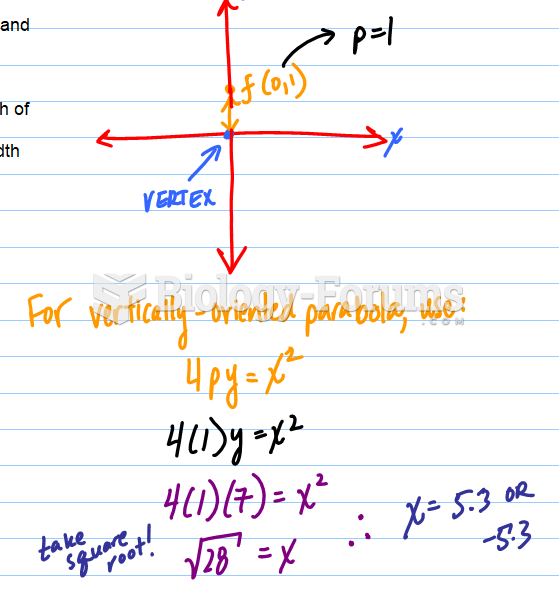
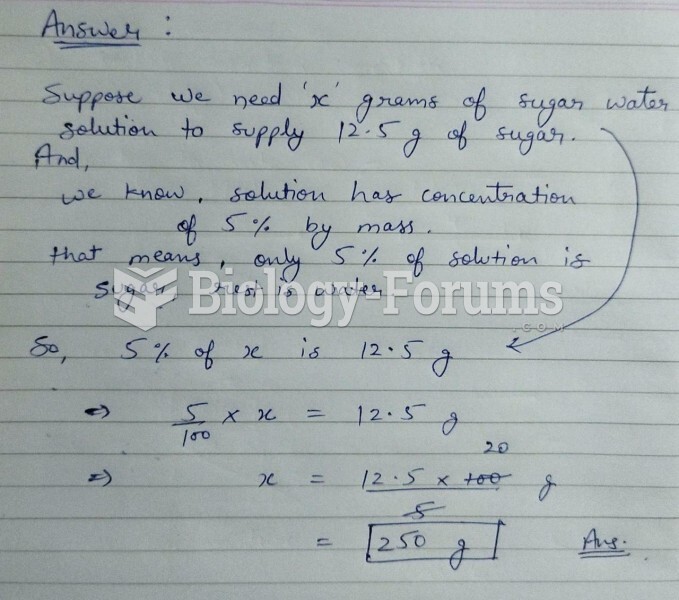
|
|
|
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
Astigmatism is the most common vision problem. It may accompany nearsightedness or farsightedness. It is usually caused by an irregularly shaped cornea, but sometimes it is the result of an irregularly shaped lens. Either type can be corrected by eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.