|
|
|
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.
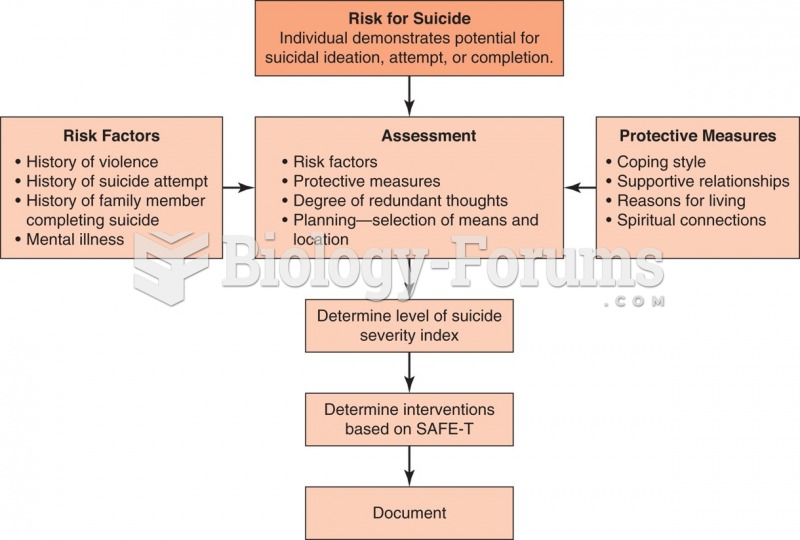
The highest suicide rate in the United States is among people ages 65 years and older. Almost 15% of people in this age group commit suicide every year.
Approximately one in three babies in the United States is now delivered by cesarean section. The number of cesarean sections in the United States has risen 46% since 1996.
In 1864, the first barbiturate (barbituric acid) was synthesized.
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.