|
|
|
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Tobacco depletes the body of vitamins A, C, and E, which can result in any of the following: dry hair, dry skin, dry eyes, poor growth, night blindness, abscesses, insomnia, fatigue, reproductive system problems, sinusitis, pneumonia, frequent respiratory problems, skin disorders, weight loss, rickets, osteomalacia, nervousness, muscle spasms, leg cramps, extremity numbness, bone malformations, decayed teeth, difficulty in walking, irritability, restlessness, profuse sweating, increased uric acid (gout), joint damage, damaged red blood cells, destruction of nerves, infertility, miscarriage, and many types of cancer.
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
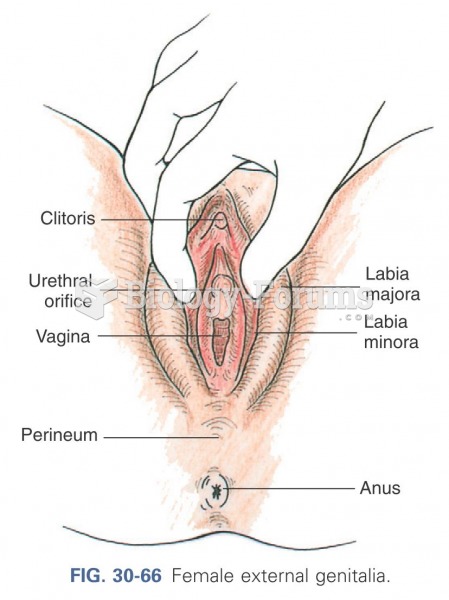
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.