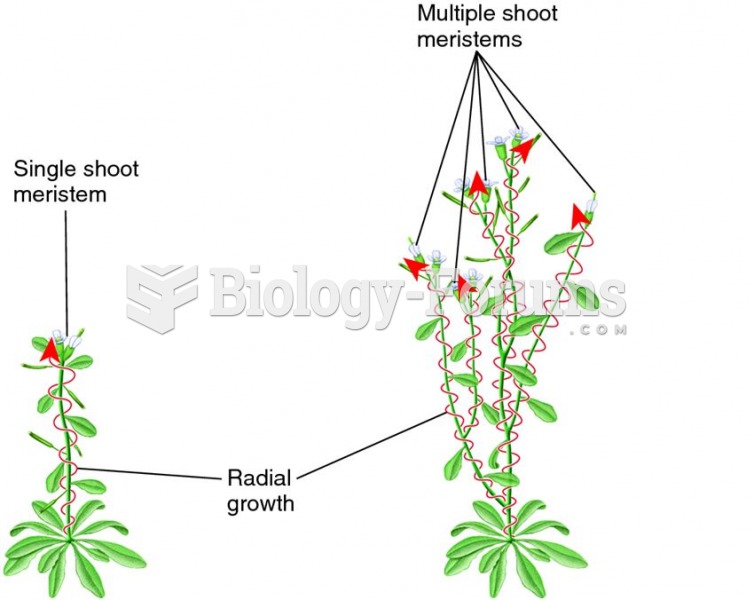
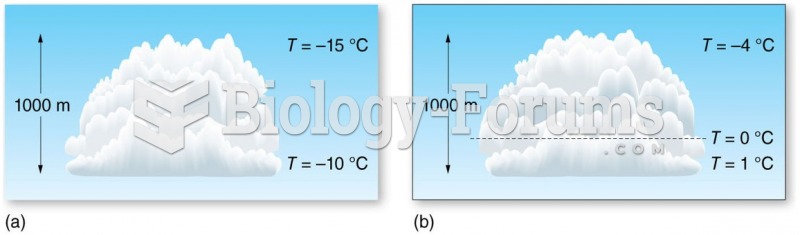
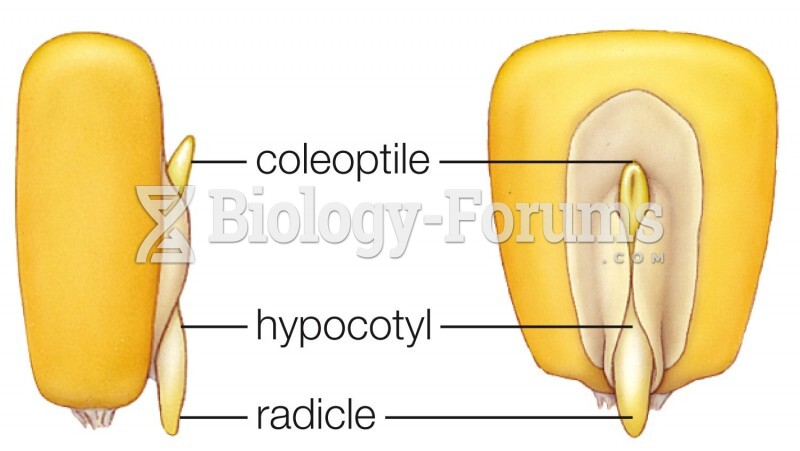
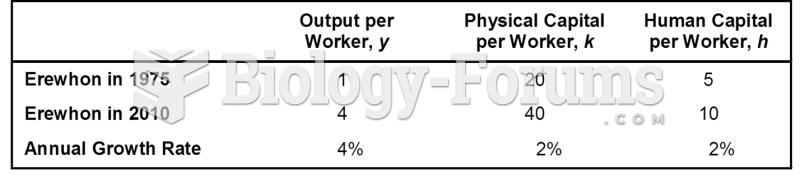|
|
|
Sildenafil (Viagra®) has two actions that may be of consequence in patients with heart disease. It can lower the blood pressure, and it can interact with nitrates. It should never be used in patients who are taking nitrates.
Intradermal injections are somewhat difficult to correctly administer because the skin layers are so thin that it is easy to accidentally punch through to the deeper subcutaneous layer.
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
Cocaine was isolated in 1860 and first used as a local anesthetic in 1884. Its first clinical use was by Sigmund Freud to wean a patient from morphine addiction. The fictional character Sherlock Holmes was supposed to be addicted to cocaine by injection.