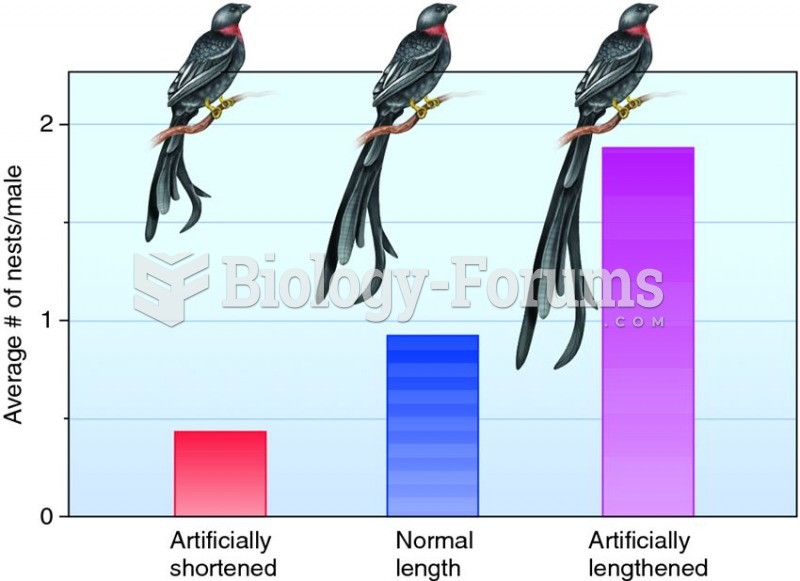
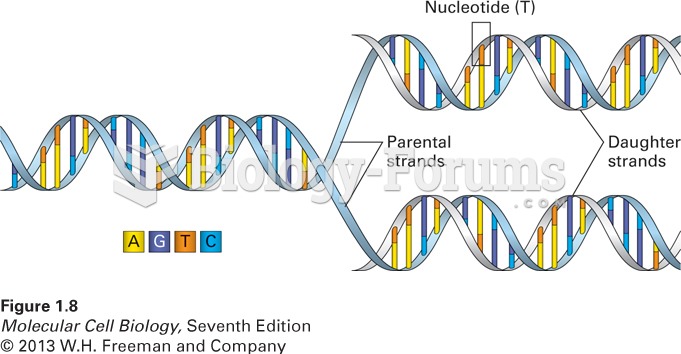
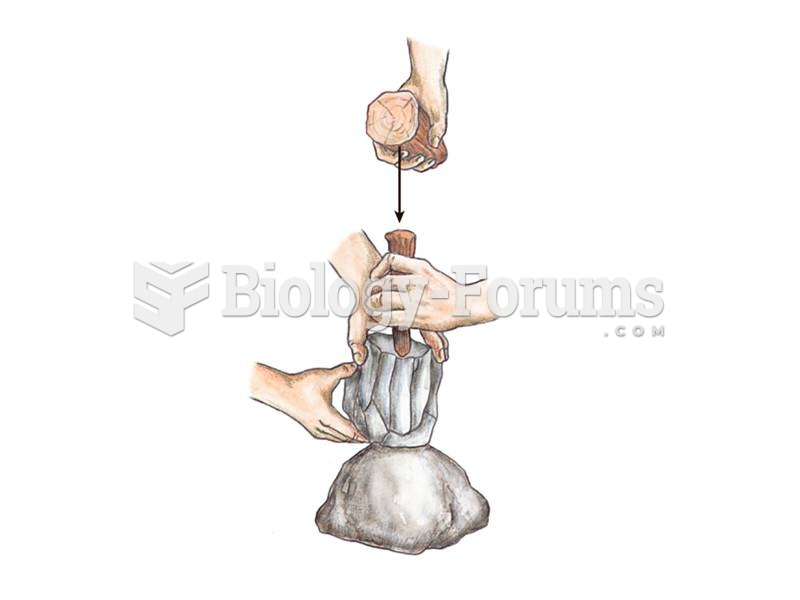
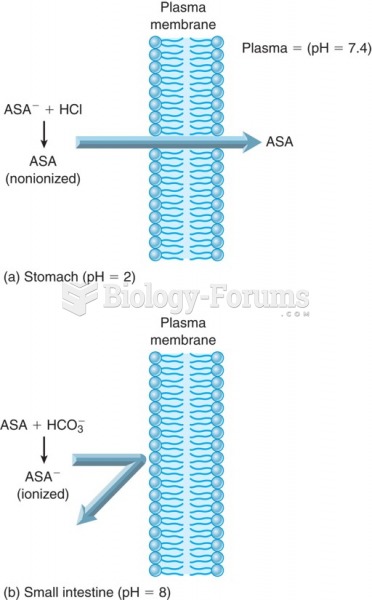
Answer to Question 1
D
Answer to Question 2
During the analysis of the customer environment, information should be collected that identifies (1 ) the firm's current and potential customers, (2 ) the prevailing needs of current and potential customers, (3 ) the basic features of the firm's and competitors' products perceived by customers as meeting their needs, and (4 ) anticipated changes in customers' needs.
Who Are Our Current and Potential Customers?-Answering the who question requires an examination of the relevant characteristics that define target markets. This includes demographic characteristics (gender, age, income, etc.), geographic characteristics (where customers live, density of the target market, etc.), and psychographic characteristics (attitudes, opinions, interests, etc.).
What Do Customers Do with Our Products?-The what question entails an assessment of how customers consume and dispose of the firm's products. Here the marketing manager might be interested in identifying the rate of product consumption (sometimes called the usage rate), differences between heavy and light users of products, whether customers use complementary products during consumption, and what customers do with the firm's products after consumption.
Where Do Customers Purchase Our Products?-The where question is associated mainly with distribution and customer convenience. Until recently, most firms looked solely at traditional channels of distribution such as brokers, wholesalers, and retailers. Thus, the marketing manager would have concerns about the intensity of the distribution effort and the types of retailers that the firm's customers patronized. Today, however, many other forms of distribution are available. The fastest growing form of distribution today is nonstore retailing-which includes vending machines; direct marketing through catalogs, home sales, or infomercials; and electronic merchandising through the Internet, interactive television, and video kiosks.
When Do Customers Purchase Our Products?-The when question refers to any situational influences that may cause customer purchasing activity to vary over time. This includes broad issues such as the seasonality of the firm's products and the variability in purchasing activity caused by promotional events or budgetary constraints.
Why (and How) Do Customers Select Our Products?-The why question involves identifying the basic need-satisfying benefits provided by the firm's products. The potential benefits provided by the features of competing products should also be analyzed. The how part of this question refers to the means of payment that customers use when making a purchase.
Why Do Potential Customers Not Purchase Our Products?-An important part of customer analysis is the realization that many potential customers choose not to purchase the firm's products. There are many potential reasons why customers might not purchase a firm's products.
This analysis is vital because the information can be used to identify and select specific target markets for the revised marketing strategy. The firm should target those customer segments where it can create and maintain a sustainable advantage over its competition.
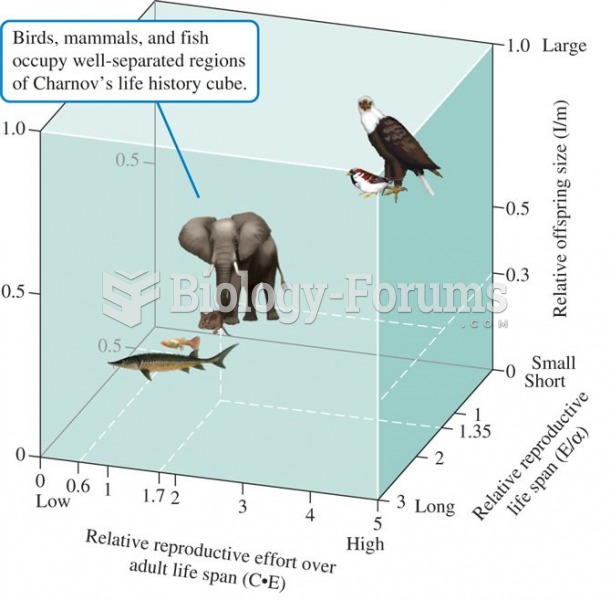 Life-history cube, a classification of fish, mammals, and altricial birds based on three dimensionle
Life-history cube, a classification of fish, mammals, and altricial birds based on three dimensionle
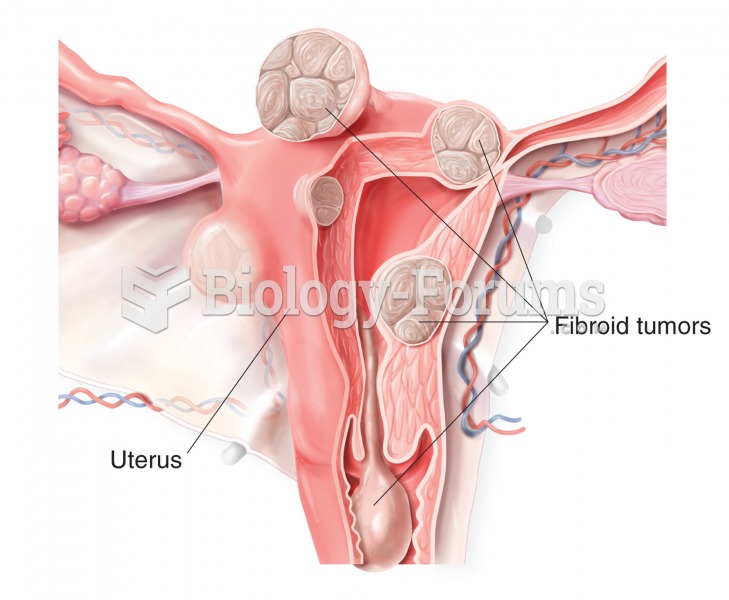 Fibroid tumors, or leiomyomas. Fibroids develop from the uterus to form a variety of hard, round ben
Fibroid tumors, or leiomyomas. Fibroids develop from the uterus to form a variety of hard, round ben