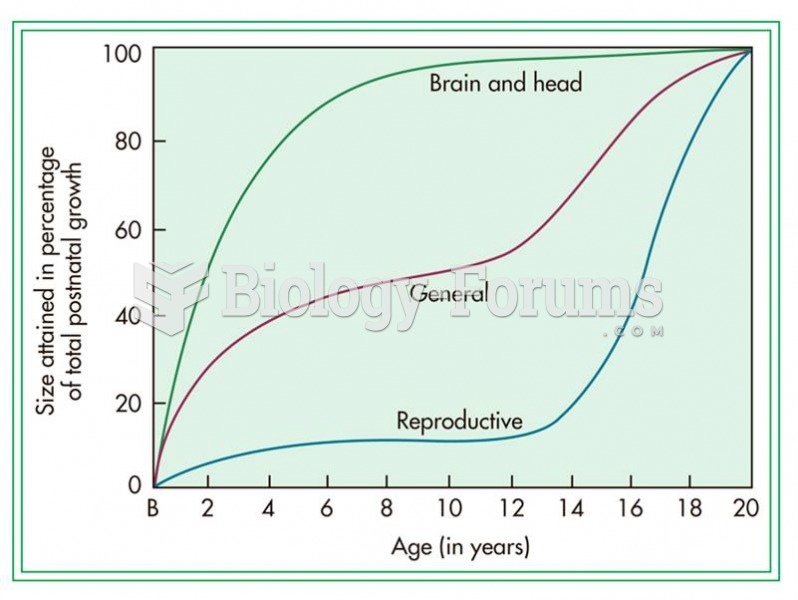
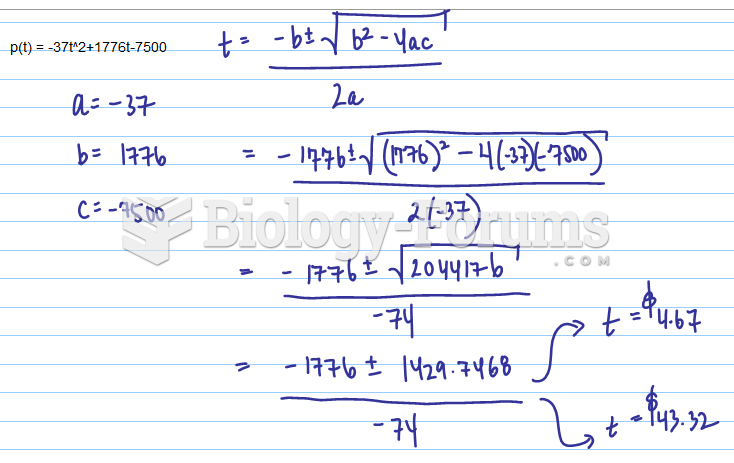
|
|
|
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
To prove that stomach ulcers were caused by bacteria and not by stress, a researcher consumed an entire laboratory beaker full of bacterial culture. After this, he did indeed develop stomach ulcers, and won the Nobel Prize for his discovery.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).