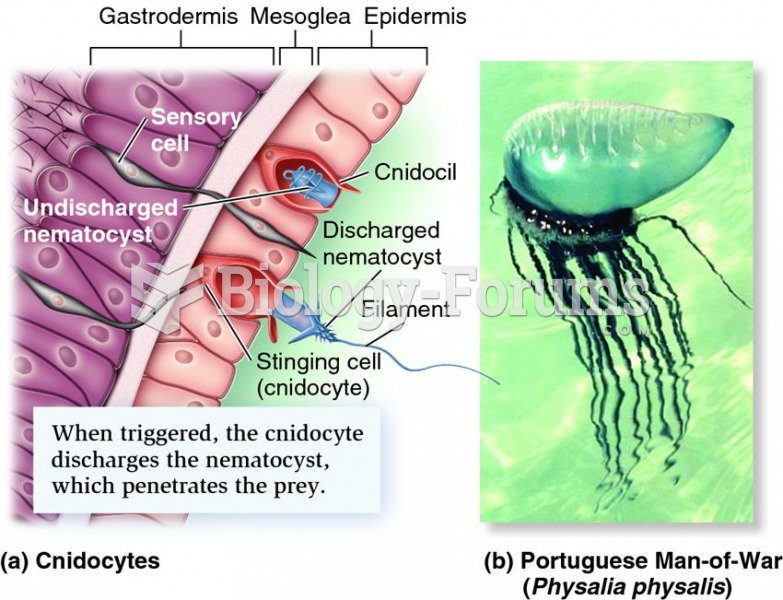
|
|
|
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
Signs and symptoms that may signify an eye tumor include general blurred vision, bulging eye(s), double vision, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye(s), iris defects, limited ability to move the eyelid(s), limited ability to move the eye(s), pain or discomfort in or around the eyes or eyelids, red or pink eyes, white or cloud spots on the eye(s), colored spots on the eyelid(s), swelling around the eyes, swollen eyelid(s), and general vision loss.
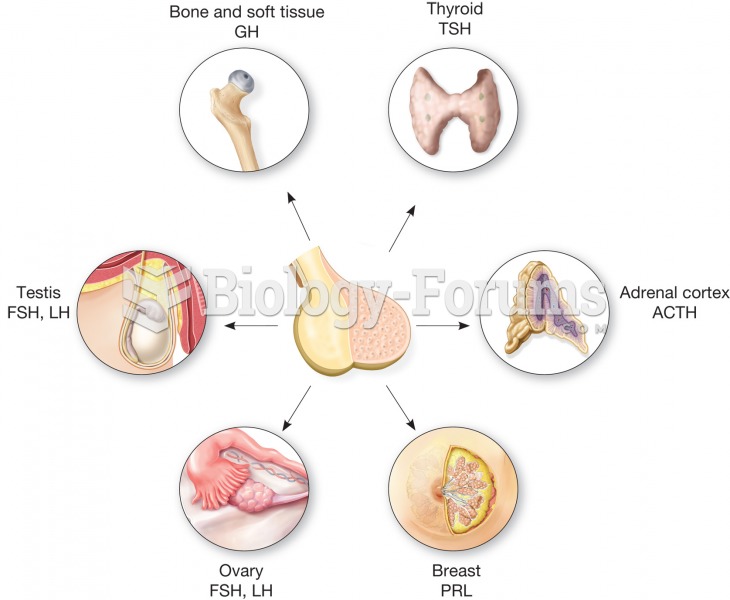 The anterior pituitary is sometimes called the master gland because it secretes many hormones that r
The anterior pituitary is sometimes called the master gland because it secretes many hormones that r
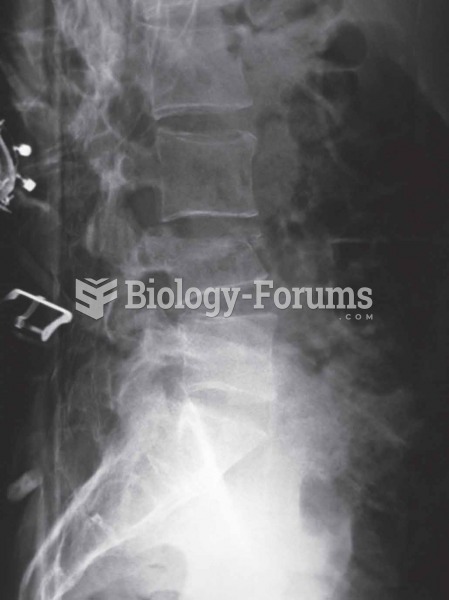 Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia
Vertebral compression Fractures of the spine (vertebra) can cause severe ”band-like” pain that radia