|
|
|
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Pope Sylvester II tried to introduce Arabic numbers into Europe between the years 999 and 1003, but their use did not catch on for a few more centuries, and Roman numerals continued to be the primary number system.
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
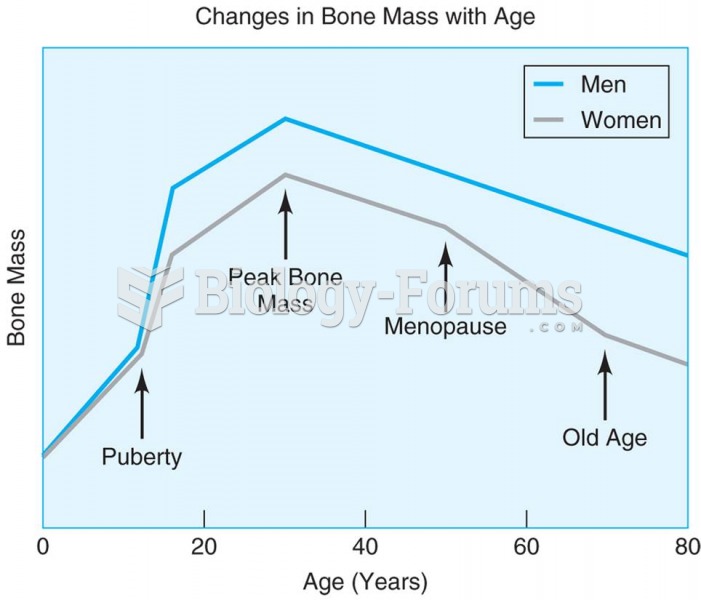 The greatest bone mass is found around age 30 for both men and women, with the later decline being f
The greatest bone mass is found around age 30 for both men and women, with the later decline being f
 To attain their goal of objectivity and accuracy in their research, sociologists must put away their ...
To attain their goal of objectivity and accuracy in their research, sociologists must put away their ...