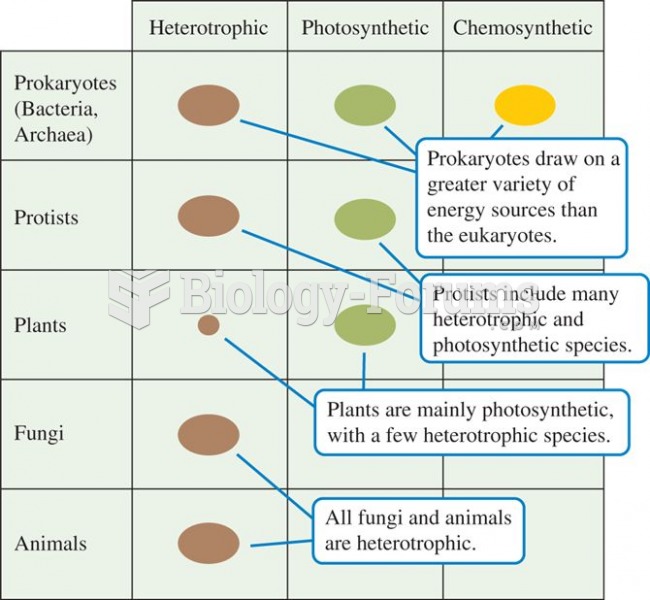
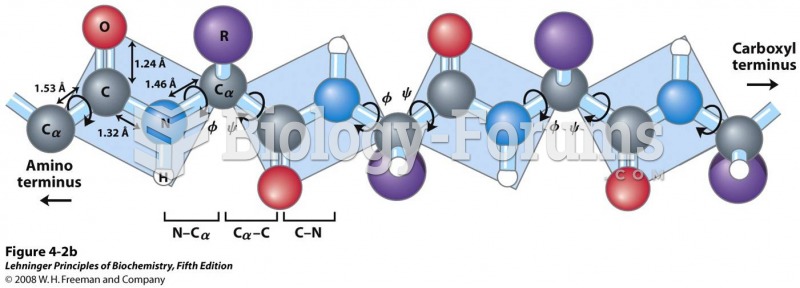
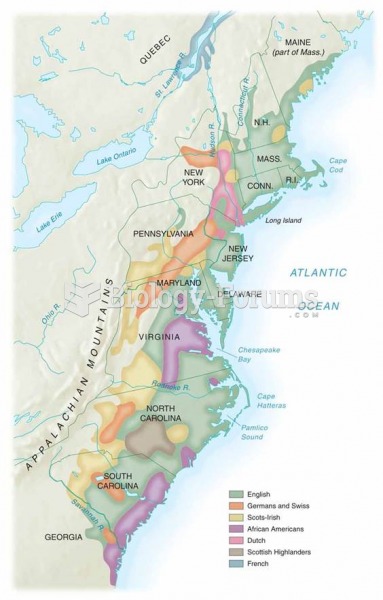
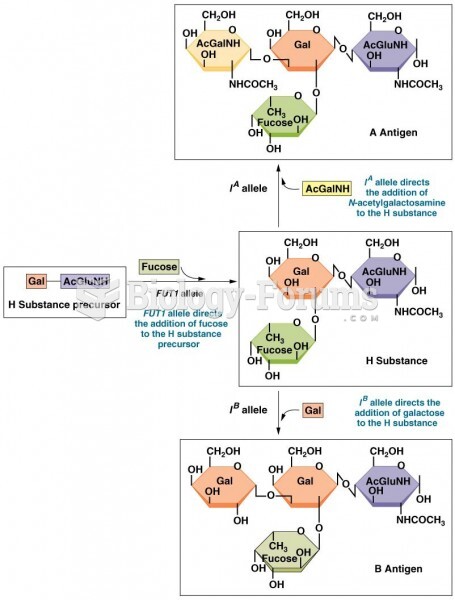
|
|
|
Egg cells are about the size of a grain of sand. They are formed inside of a female's ovaries before she is even born.
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.