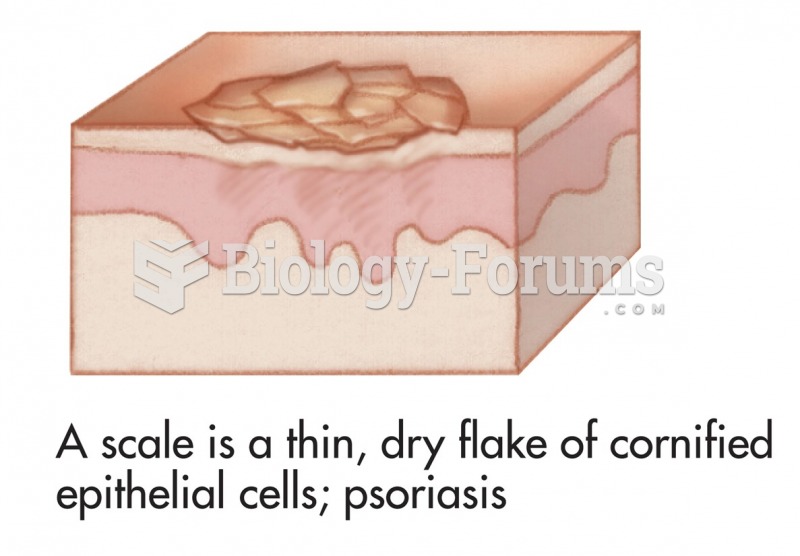
|
|
|
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
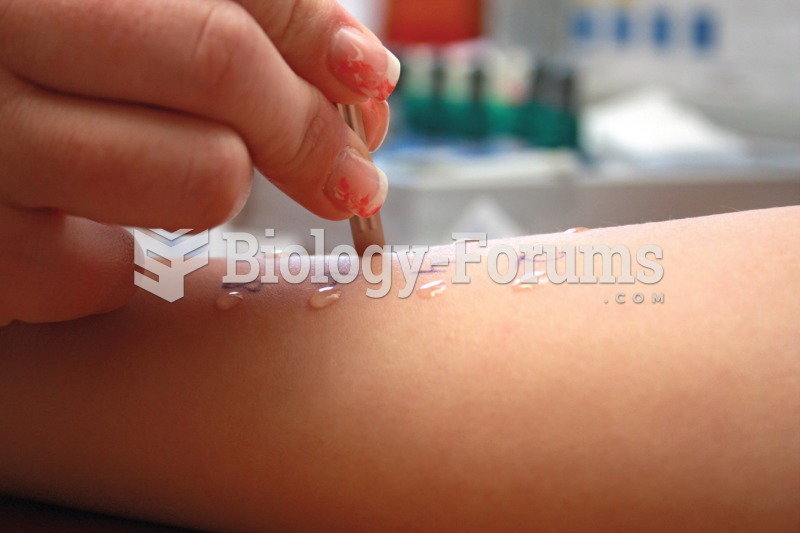 The patient is undergoing an allergy skin test by receiving subdermal inoculations of allergens. Inf
The patient is undergoing an allergy skin test by receiving subdermal inoculations of allergens. Inf
 A William Jennings Bryan poster alludes to religion: “no crown of thorns” and no “cross of gold.” Br
A William Jennings Bryan poster alludes to religion: “no crown of thorns” and no “cross of gold.” Br