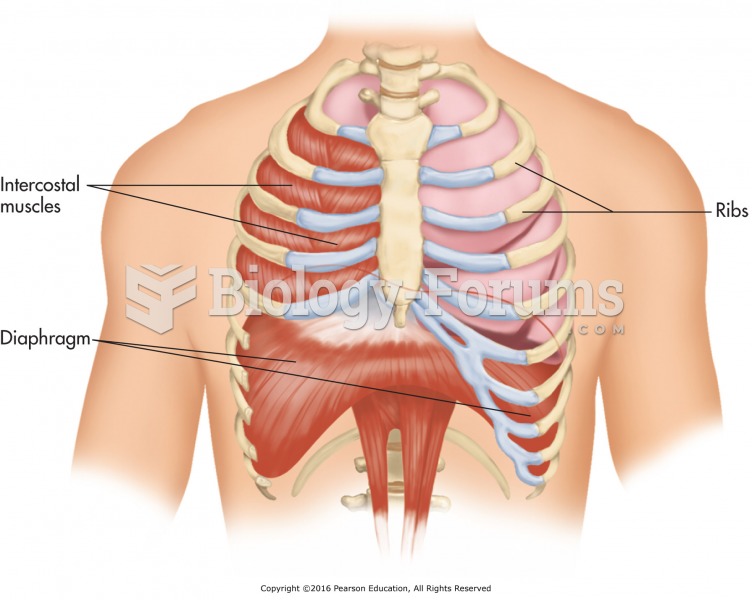
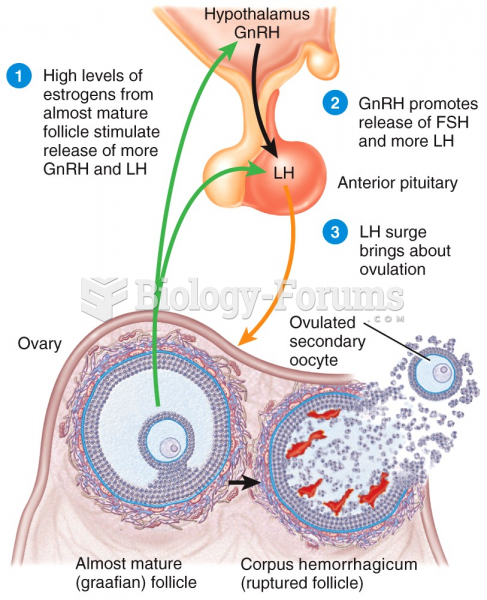
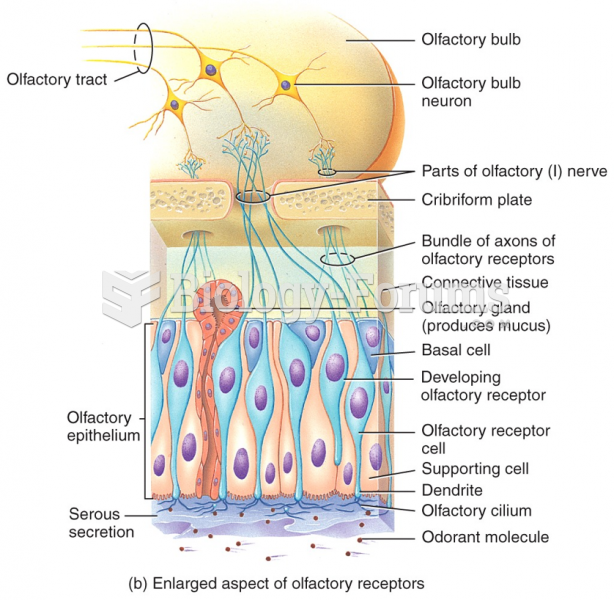
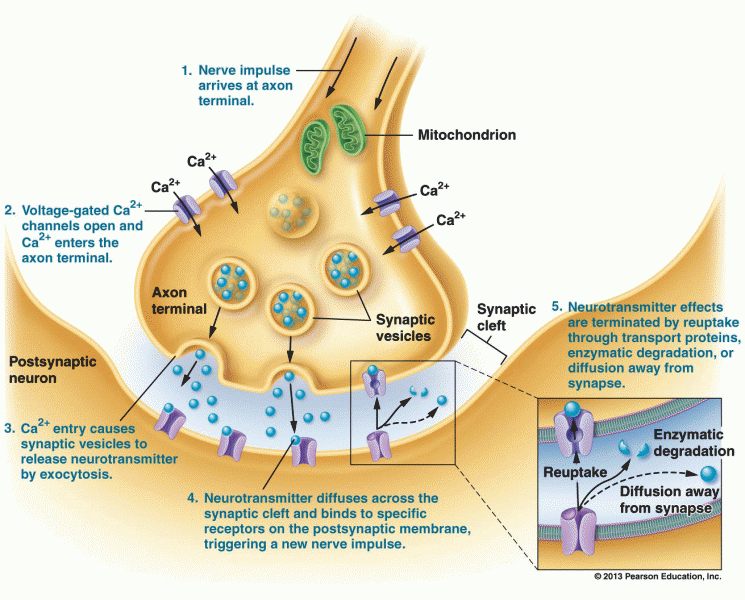
|
|
|
More than 20 million Americans cite use of marijuana within the past 30 days, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). More than 8 million admit to using it almost every day.
Most women experience menopause in their 50s. However, in 1994, an Italian woman gave birth to a baby boy when she was 61 years old.
As many as 20% of Americans have been infected by the fungus known as Histoplasmosis. While most people are asymptomatic or only have slight symptoms, infection can progress to a rapid and potentially fatal superinfection.
Approximately 500,000 babies are born each year in the United States to teenage mothers.
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.