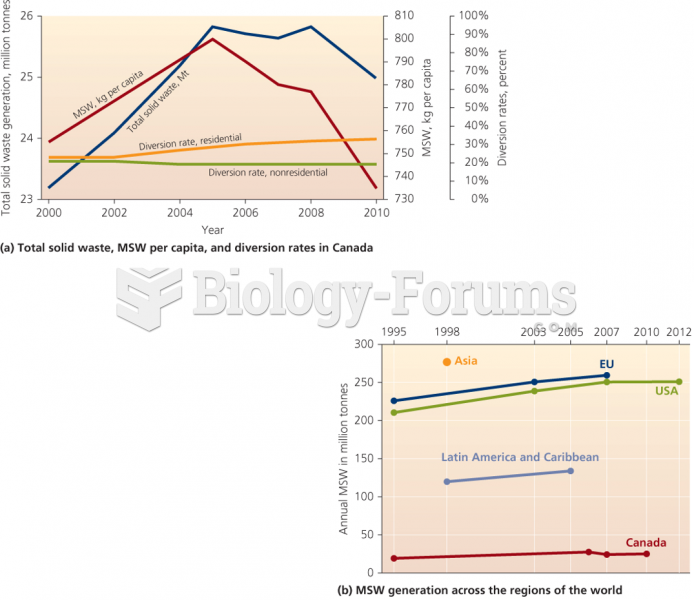
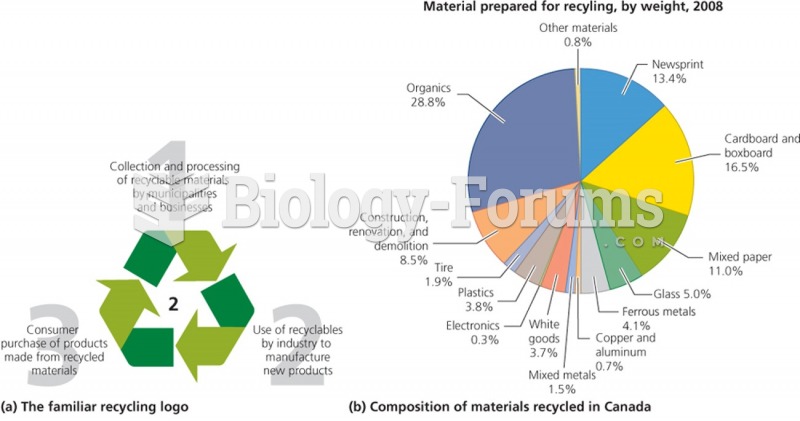
|
|
|
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Calcitonin is a naturally occurring hormone. In women who are at least 5 years beyond menopause, it slows bone loss and increases spinal bone density.
Drugs are in development that may cure asthma and hay fever once and for all. They target leukotrienes, which are known to cause tightening of the air passages in the lungs and increase mucus productions in nasal passages.
There are over 65,000 known species of protozoa. About 10,000 species are parasitic.
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.