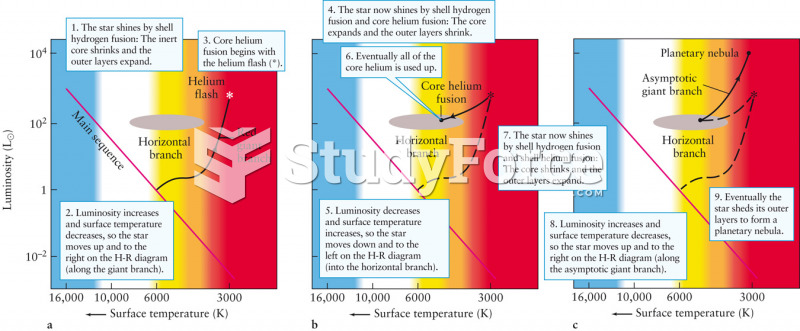
Answer to Question 1
1) Strategic priorities -> Goals and 2) Goals -> Strategic priorities
Answer to Question 2
(Sample answer: Discussion of any four intentional or unintentional rating errors and proposed solutions according to the text are acceptable.)
- Similar to me error. Similarity leads to attraction so that we tend to favor those who are similar to us. Consequently, in some cases supervisors are more likely to give higher performance ratings to those employees who are perceived to be more similar to them in terms of attitudes, preferences, personality, and demographic variables including race and gender.
- Contrast error. This error occurs when, even when an absolute measurement system is in place, supervisors compare individuals with one another instead of against predetermined standards. This error is most likely to occur when supervisors complete multiple appraisal forms at the same time, because in such situations it is difficult to ignore the ratings given to other employees.
- Halo error. This error occurs when raters fail to distinguish among the different aspects of performance being rated. So, if an employee receives a high score on one dimension, he/she also receives a high score on all other dimensions even though performance may not be even across dimensions. This error is typically caused by the supervisor's assigning performance ratings based on an overall impression about the employee instead of evaluating each performance dimension independently.
- Primacy error. Primacy error occurs when performance evaluation is influenced mainly by information collected during the initial phases of the review period.
- Recency error. This error occurs when performance evaluation is influenced mainly by information gathered during the last portion of the review period.
- Leniency error. Leniency error occurs when raters assign high (lenient) ratings to most or all employees. In other words, leniency involves artificial rating inflation.
- Severity error. Severity error occurs when raters assign low (severe) ratings to most or all employees. That is, severity involves artificial rating deflation.
- Central tendency error. Central tendency error occurs when raters use only the middle points on the rating scales and avoid using the extremes. The result is that most or all employees are rated as average.
- Negativity error. Negativity error occurs when raters place more weight on negative information than on positive or neutral information.
- First impression error. First impression error occurs when raters make an initial favorable or unfavorable judgment about an employee and then ignore subsequent information that does not support the initial impression.
- Spillover error. Spillover error occurs when scores from previous review periods unjustly influence current ratings.
- Stereotype error. Stereotype error occurs when a supervisor has an oversimplified view of individuals based on group membership. This type of error can also lead to biased evaluations of performance when an individual (e.g., woman) violates stereotypic norms by working in an occupation that does not fit the stereotype (e.g., assembly of airplane parts). This type of error can also result in consistently lower performance ratings for members of certain groups.
- Attribution error. The attribution error takes place when a supervisor attributes poor performance to an employee's dispositional tendencies (e.g., personality and abilities) instead of features of the situation (e.g., malfunctioning equipment).
To reduce these errors, I would implement a combination of FOR and BO training. The frame of reference would help employees have a picture of what performance looks like and how others in the company are rating it. This will help when rating performance. I would also implement a BO training to help people learn how to document performance over the course of the year so that performance review meetings go smoothly and are based on examples of actual performance, not personal biases.