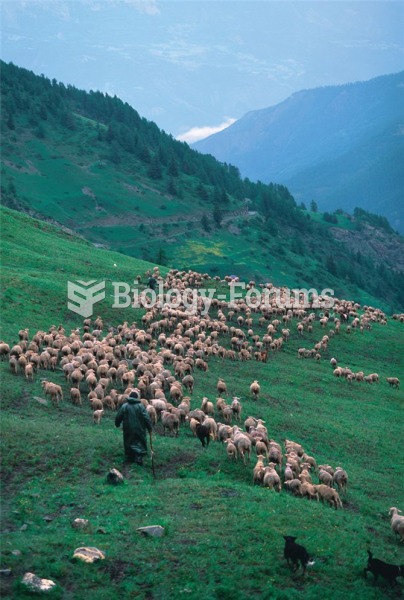
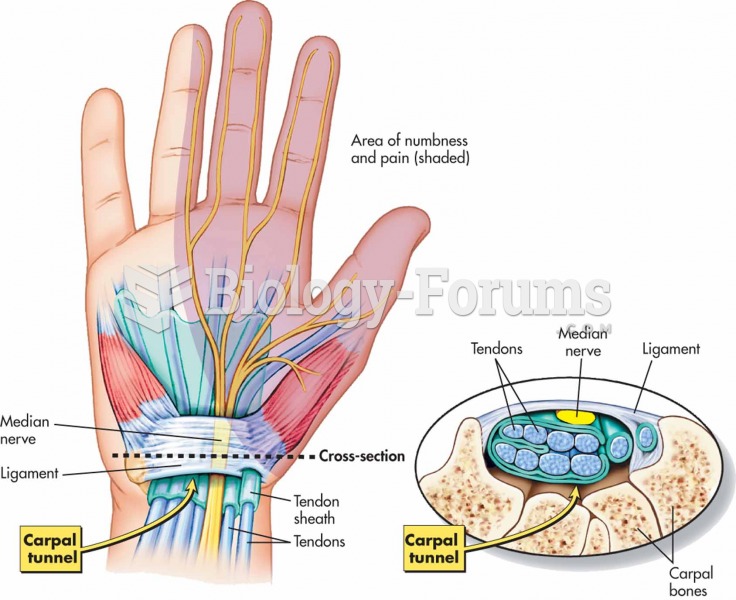
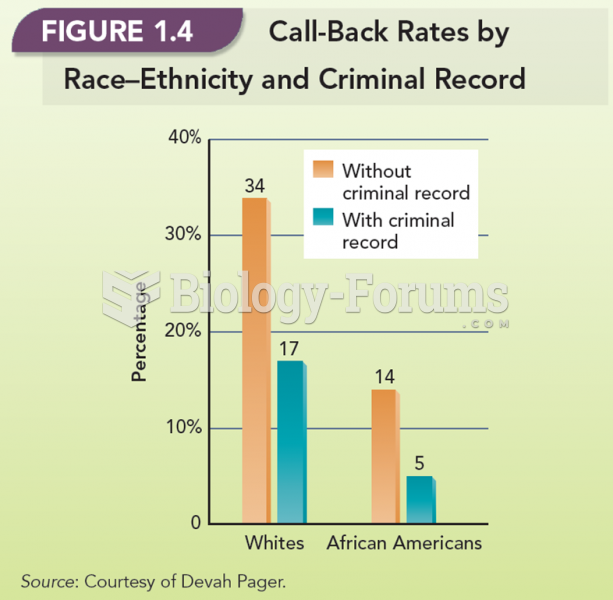
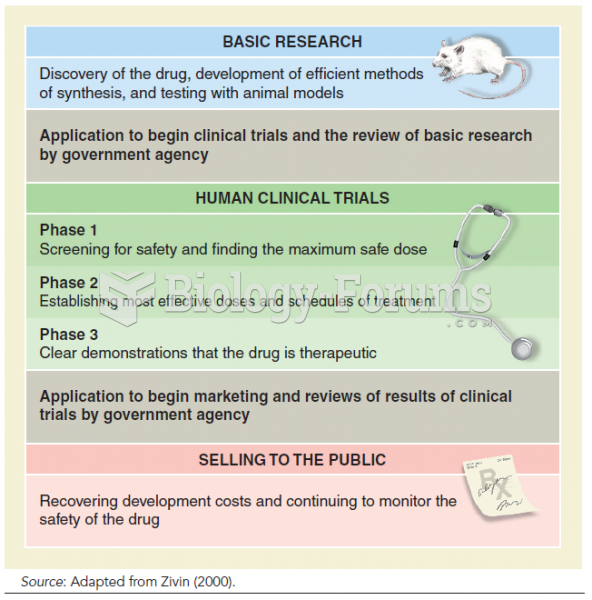
Answer to Question 1
The project management process occurs in four phases. Each phase requires that several activities be performed. The four phases include initiating the project, planning the project, executing the project, and closing down the project. Each of the four phases is briefly highlighted below. The first phase, project initiation, includes activities that are performed to assess the size, scope, and complexity of the project and to establish procedures to support later project activities. Project initiation activities include establishing the project initiation team, establishing a relationship with the customer, establishing the project initiation plan, establishing management procedures, establishing the project management environment and project workbook, and developing the project charter.
Project planning, the second phase, focuses on defining clear, discrete activities and the work needed to complete each activity within a single project. Varied and numerous types of tasks are performed during this phase. Project planning activities include describing project scope, alternatives, and feasibility; dividing the project into manageable tasks; estimating resources and creating a resource plan; developing a preliminary schedule; developing a communication plan; determining project standards and procedures; identifying and assessing risk; creating a preliminary budget; developing a project scope statement; and setting a baseline project plan.
Project execution, the third phase of the project management process, is the phase in which the plans created in the prior phases are put into action. Project execution activities include executing the baseline project plan, monitoring project progress against the baseline project plan, managing changes to the baseline project plan, maintaining the project workbook, and communicating the project status. The final phase of the project management process, project closedown, focuses on bringing a project to an end. Project closedown activities include closing down the project, conducting postproject reviews, and closing the customer contract.
Answer to Question 2
C
Explanation: C) A tangible benefit is derived from the creation of an information system that can be measured in dollars and with certainty. A savings of 5,000 resulting from a data entry error reduction would be an example of a tangible benefit.
CL