|
|
|
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
Atropine, along with scopolamine and hyoscyamine, is found in the Datura stramonium plant, which gives hallucinogenic effects and is also known as locoweed.
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
 The world has been horrified recently at a U.S. Congress so polarized and paralyzed that it cannot p
The world has been horrified recently at a U.S. Congress so polarized and paralyzed that it cannot p
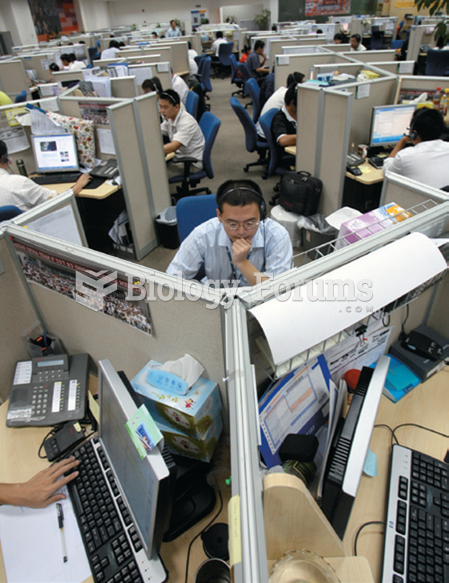 Durkheim believed that modern societies produce feelings of isolation, much of which come from the ...
Durkheim believed that modern societies produce feelings of isolation, much of which come from the ...