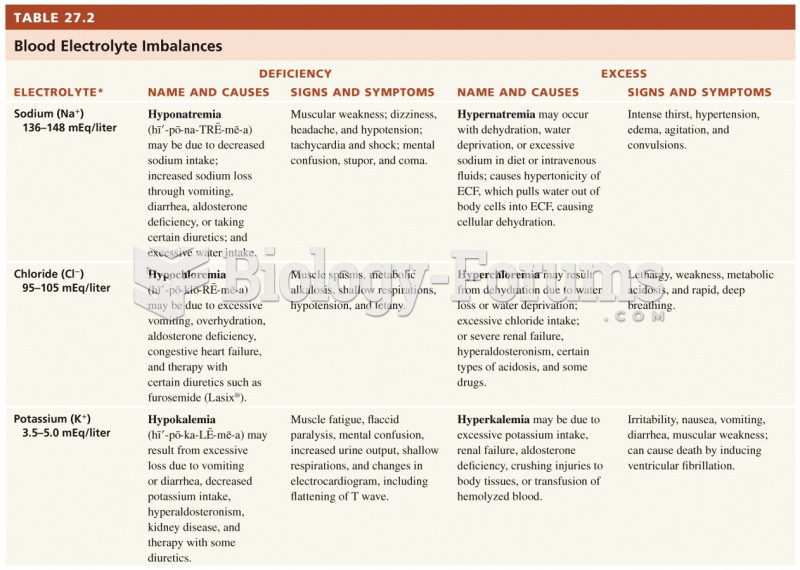
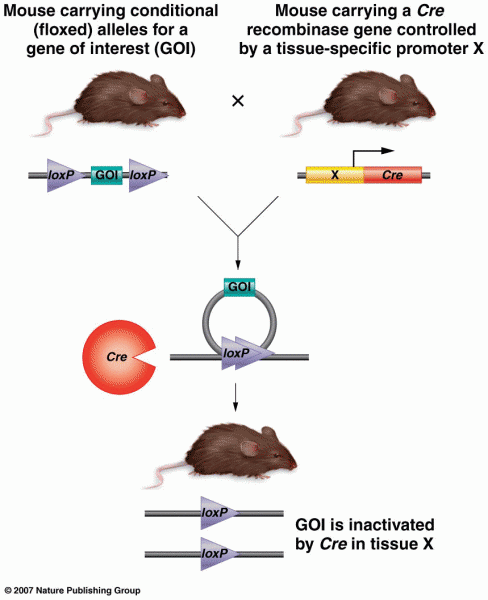
|
|
|
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
The most common childhood diseases include croup, chickenpox, ear infections, flu, pneumonia, ringworm, respiratory syncytial virus, scabies, head lice, and asthma.