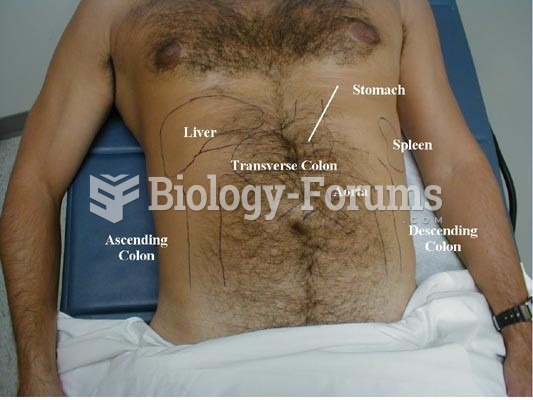
|
|
|
About 600,000 particles of skin are shed every hour by each human. If you live to age 70 years, you have shed 105 pounds of dead skin.
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).