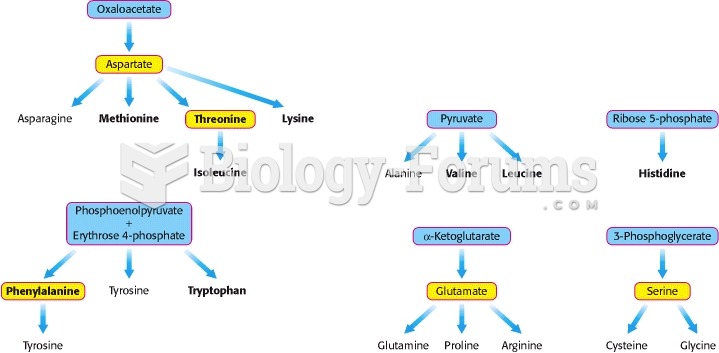
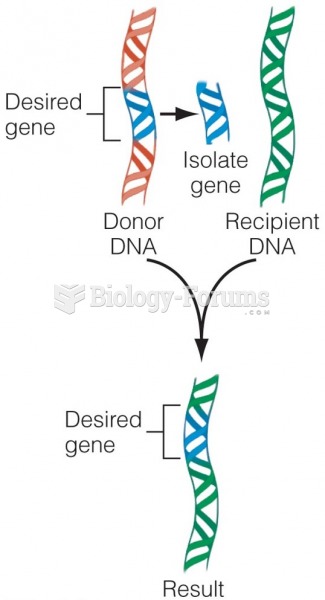
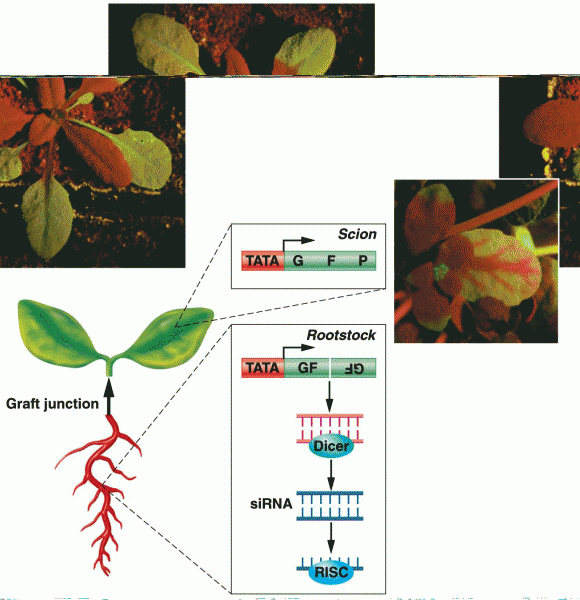
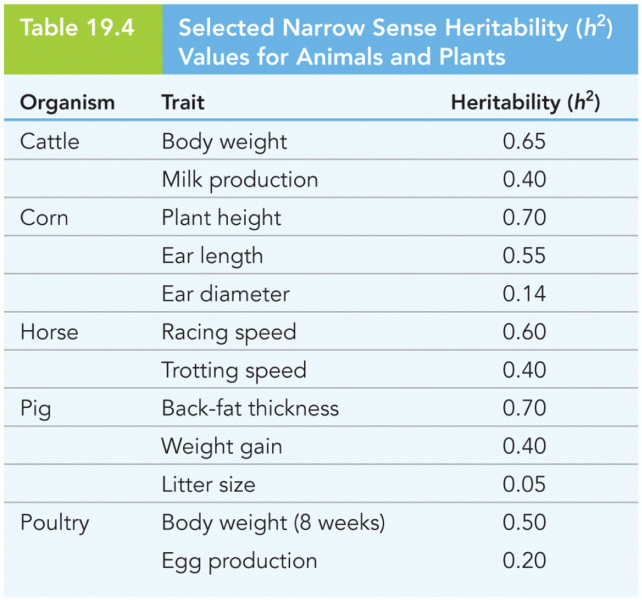
Answer to Question 1
The answers to these questions will vary depending upon the area of the country. (a) Ecological succession may be caused by grass fires (near a road, next to picnic areas), erosion (construction sites, logging, agricultural fields), clearing of land (building construction, road building), or demolition of buildings. Once you have identified possible ecological succession causes, it will be possible to consider the plant and animal changes that may have taken place. For example, grasses, pine trees, or invasive species could be favored. (b) Population balance mechanisms that should be considered are territoriality, interspecies plant competition, missing predators, and grazing by herbivores. Most species will not be directly impacted if another species is removed or introduced. You will see direct impacts if the species removed is a food source, a competitor, a predator, and
so forth. You will see direct impacts from an introduced species if the introduced species competes for the same food, eats or provides food for the species you are evaluating, or competes for such needs as nesting sites and territory.
Answer to Question 2
Student responses will vary. Students should discuss possible renewable resource options listed in this chapter, including conservation by Earth sheltering, solar power, wind power, and other types of power that can be used in commercial facilities.
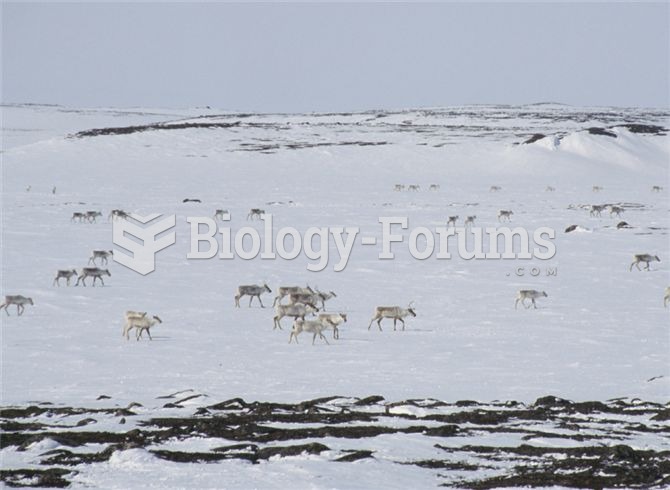
Answer to Question 3
This type of biome would be described as tundra. Because of the relatively low amount of precipitation in the area and cold temperatures (causing freezing through most of the year), the main producers that would be able to survive in this biome would be low-growing sedges, dwarf shrubs, lichens, mosses, and grasses. Consumers would include lemmings, arctic hares, arctic foxes, lynx, caribou, insects, and migrant shorebirds.