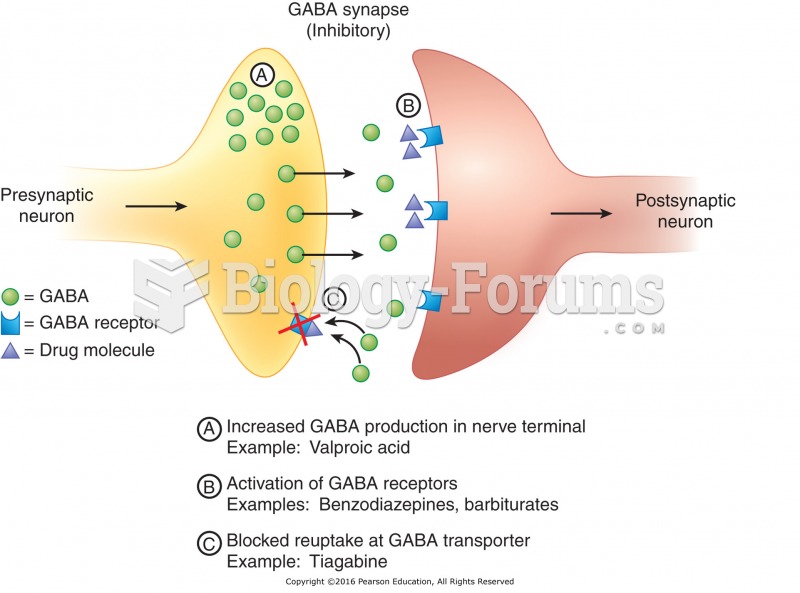
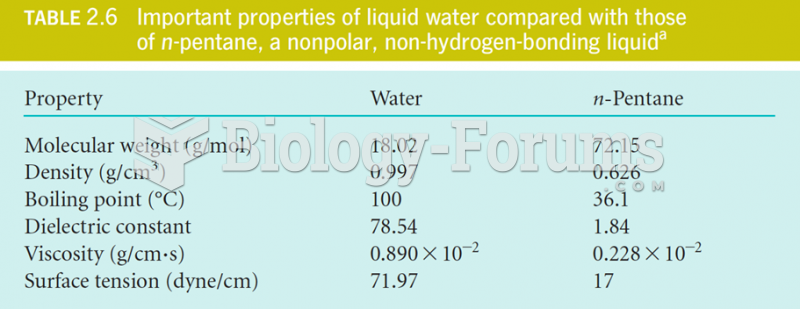
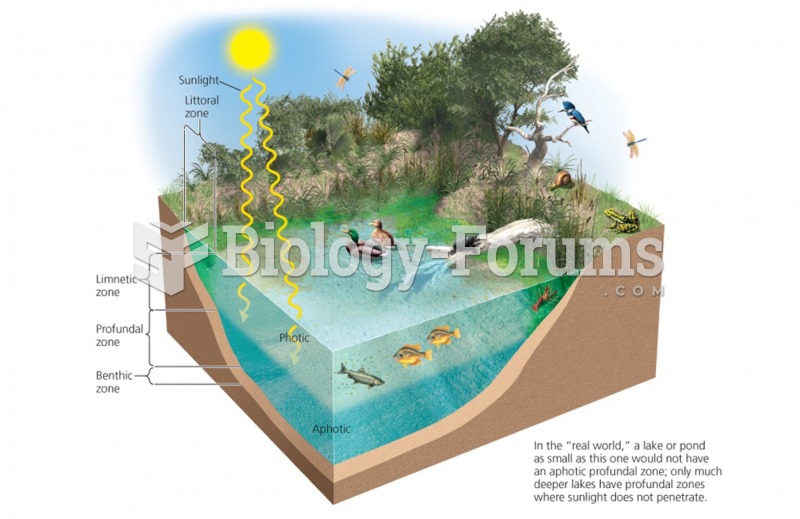
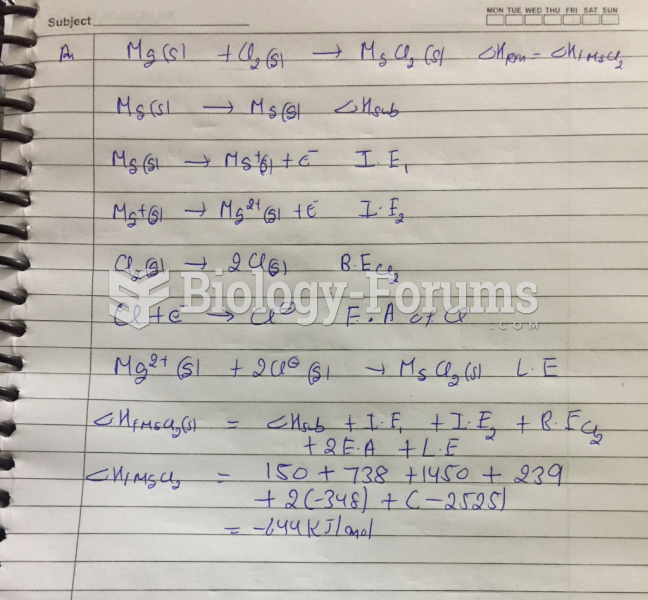
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Illicit drug use costs the United States approximately $181 billion every year.
Did you know?
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
Did you know?
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
Did you know?
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Did you know?
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.