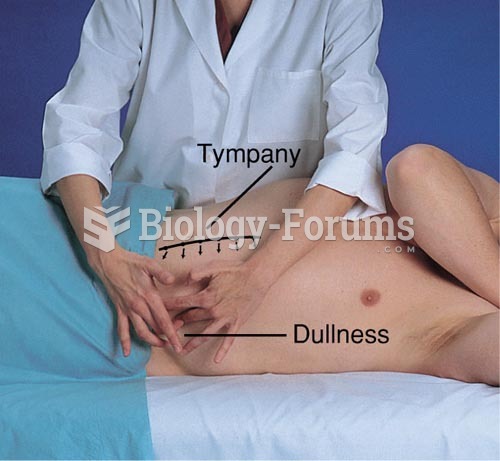
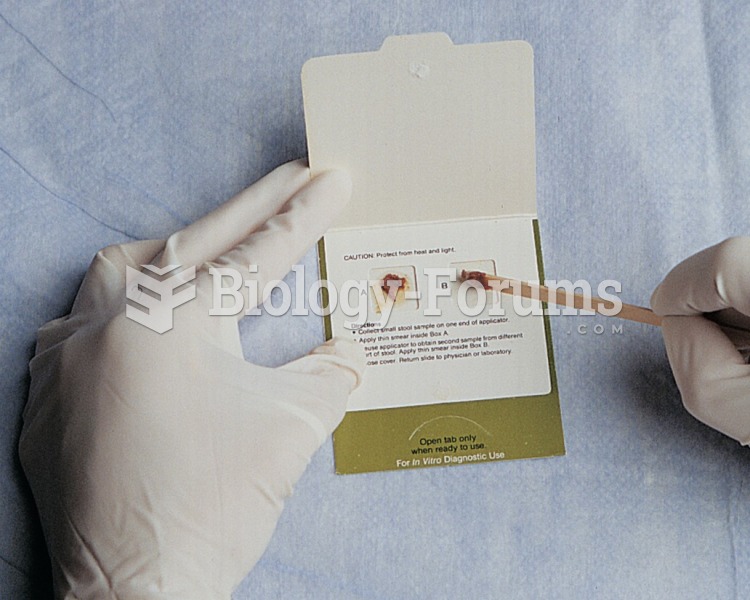
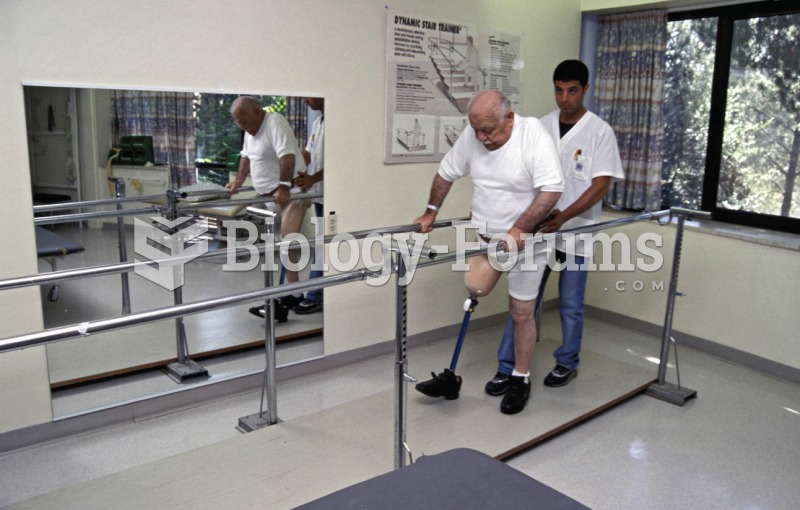
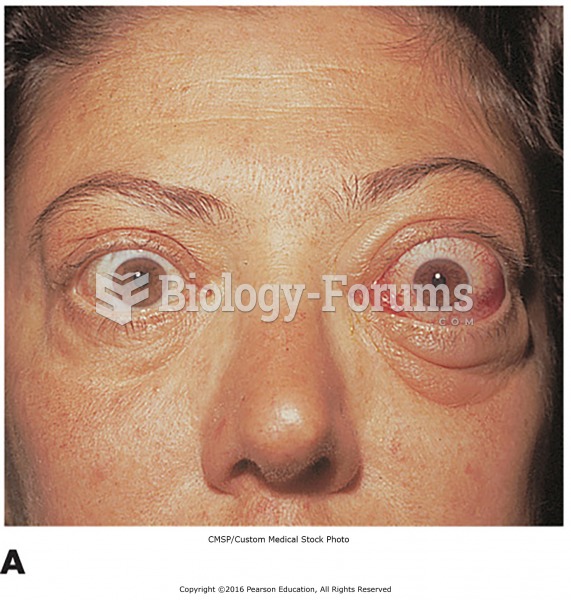
|
|
|
Urine turns bright yellow if larger than normal amounts of certain substances are consumed; one of these substances is asparagus.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.