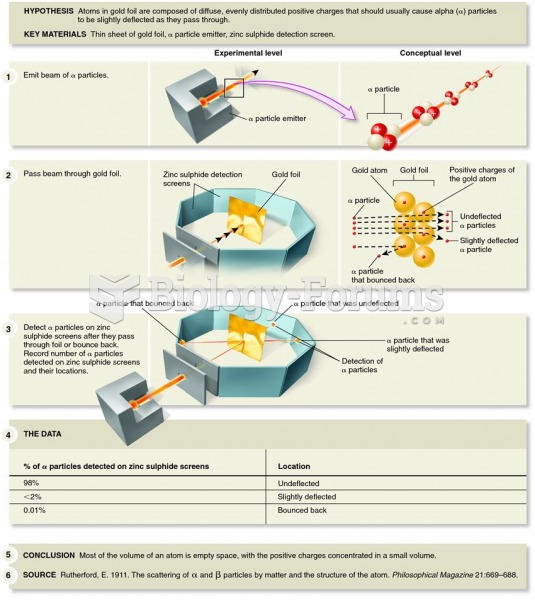
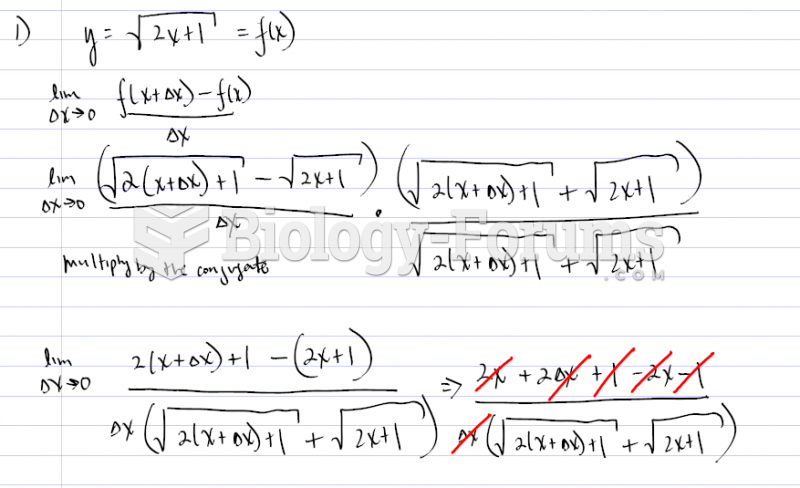
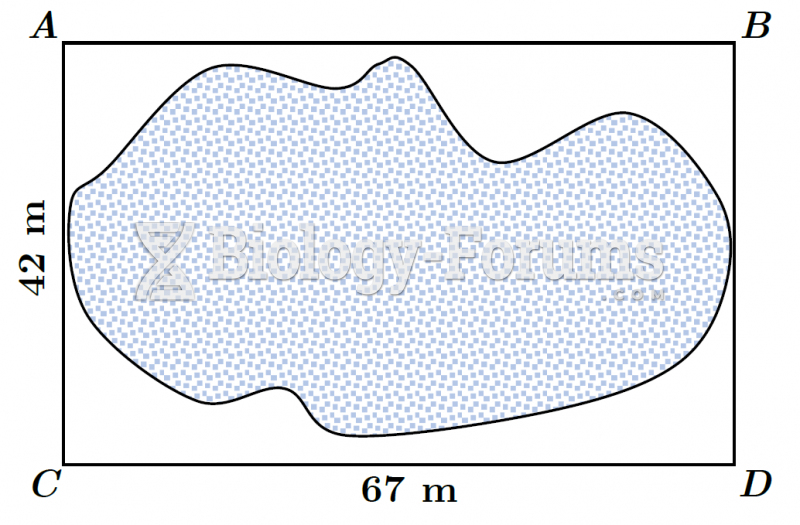
|
|
|
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
Every flu season is different, and even healthy people can get extremely sick from the flu, as well as spread it to others. The flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May. Every person over six months of age should get an annual flu vaccine. The vaccine cannot cause you to get influenza, but in some seasons, may not be completely able to prevent you from acquiring influenza due to changes in causative viruses. The viruses in the flu shot are killed—there is no way they can give you the flu. Minor side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given. It is possible to develop a slight fever, and body aches, but these are simply signs that the body is responding to the vaccine and making itself ready to fight off the influenza virus should you come in contact with it.
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.