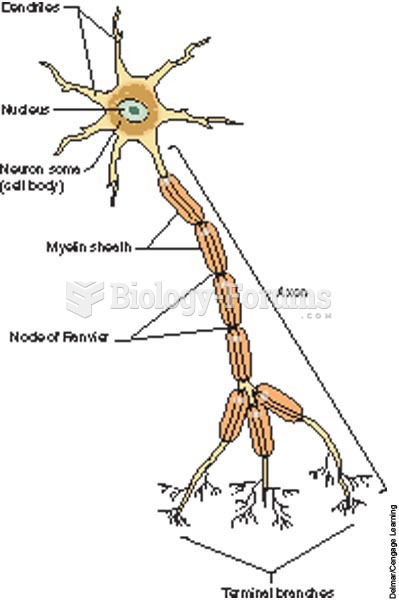
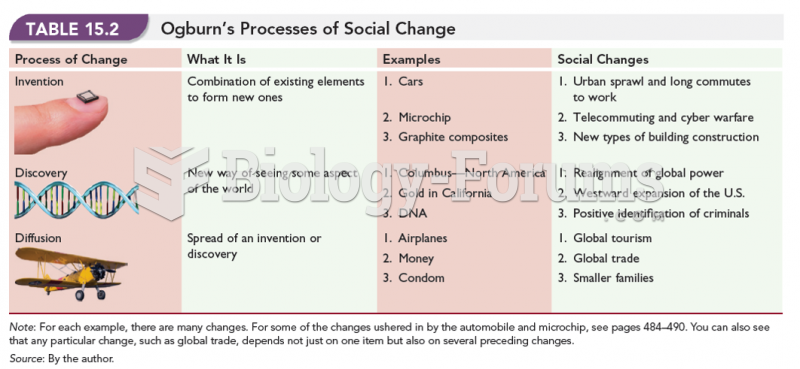
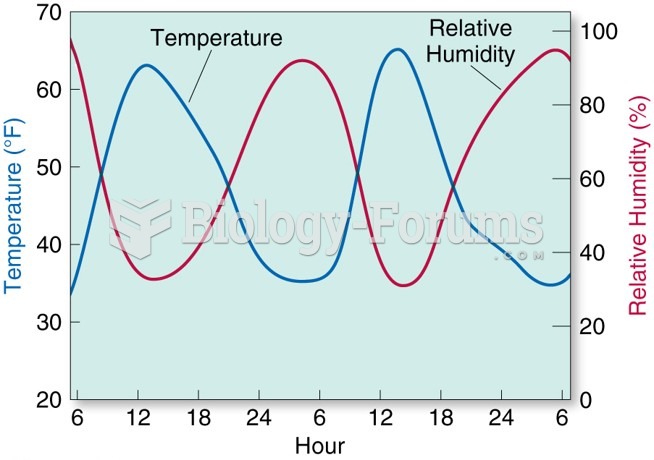
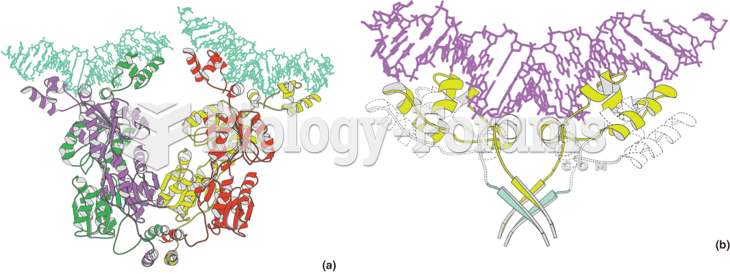
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
Did you know?
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Did you know?
Eating carrots will improve your eyesight. Carrots are high in vitamin A (retinol), which is essential for good vision. It can also be found in milk, cheese, egg yolks, and liver.
Did you know?
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
Did you know?
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.